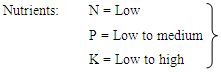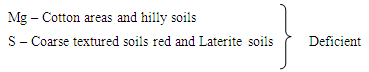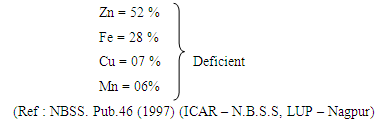|
||||||
Resource Mananagement :: Soil :: Soil Resources of TN |
||||||
Earth needs to be nurtured with mother’s care because, Earth gives everything for sustaining life. Soils that form one of the most precious natural resources of earth. For sustainable agricultural production, it is necessary to focus attention on the soil and climate resource base, current status of soil degradation and soil-based agrotechnology for optimizing land use. India lives in villages and agriculture forms the back bone of the Country’s economy. Tamil Nadu is the Southern most state of India. It is located between 8.05’ and 13.34’ North latitudes and 76.14’ and 80.21 East longitudes. It covers an area of about 13 Mha and accounts for about 4 per cent of the total geographical area of the country. The Tamil Nadu State forms part of the peninsular shield and composed of geologically ancient rock of diverse orgins (i.e different soils). About three – fourth of the area of the state is unclassified crystalline rocks of Archaeon age and the rest is sedimentary rocks. The State can broadly be divided into three major physiographic divisions and 10 land forms. The climate is Semi-arid in the plains and humid to Sub-humid in the hills with annual rainfall from 750 mm in some parts of the plains to over 2400 mm in the high hills. In all 94 soil families, classified in to six orders. Soil depth is not a limiting factor for crop growth in Tamil Nadu (14% shallow and very shallow soils of a TGA of the state). The texture of soils of Tamil Nadu covers a wide range from sand to clay (18% sandy surface 53% loamy and 22% clay). The soil drainage is not a major problem for crop production in the state (14% poorly to imperfectly drained soils, 64% moderately drained to well drained soil and 15% of TGA excessively drained soils). The soil calcareousness affects 34 per cent of the area in the Tamil Nadu State. Regarding Land Capability classification in Tamil Nadu, 79 per cent of the area is suitable for cultivation and 21 per cent of the area is not suitable for cultivations. Of the lands suited for cultivation, good land (class II) covers about 34 per cent, moderately good land (class III) covers about 30 per cent and fairly good land (class IV) covers an out of 15 per cent of the area of the state. In Tamil Nadu State, about 77 per cent of the area is suitable for irrigation with varying degree of limitation. Physical constraints: No physical constraints : 55%
|
||||||
| Home | Seasons & Varieties | Tillage | Nutrient Management | Irrigation Management | Weed Management | Crop Protection | Cost of Cultivation | © All Rights Reserved. TNAU-2013. |
||||||