Garlic cultivation in natural farming methods
Varieties
Mettupalayam type (100 days)
Ooty 1 (130 days)
Season
Karpokam: (April - May)
Kataipokam: (October - November)
Soil and weather:
Silt clay loam soil with water filter facility is suitable for cultivation. Cold weather is enough for cultivation.
Seed and Seeding:
To plough the land. Bars can be prepared 15 cm space. Planting should be done at 7.5 cm space.
Seed rate: 1750 kg / ha
Seed treatment:
Garlic seeds should be dip 1 hour with 3% Panchagavya, tacakavya, 4% Pseudomonas florasence, 4% Trichoderma viride, 4% Azospirillum and 4% Phosphobacteria solution and then dry it in shade.
Fertilizer application
-
Planting the Green fertilizer and lupine in the field and soil tillage should be done at the time of flowering.
-
Well-decomposed farmyard manure 50 t / ha can be applied while preparing to land at the scale.
-
Biologically decomposed manure 5 ton / ha can be applied while preparing the land.
-
Vermicompost 5 tons / ha to be applied when preparing to land at the scale.
-
5 tons of mushroom compost manure is to be applied. Also Phospobacteria, Azospirillum 5kg/ha with 50kg well decomposed farmyard manure can be applied while preparing the land.
-
Cowdug manure 75g/ha mix with 40 L water and make a solution and spray this solution while preparing the land.
|
 |
 |
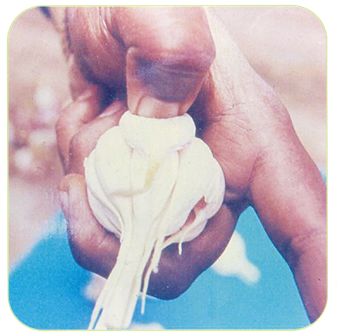
| Harvested garlic |
|
Growth regulators
-
Panchgavya and dasakavya 3% solution is to spray 3 times for 15 days.
-
10 % vermicompost fertilizer a month after sowing Dithering to spray 3 times at intervals of 15 days.
-
Cow horn silica: 250 g / ha dissolved in 100 liters of water to spray for foliar application at the 65th day after planting.
-
Manchariyan tea extracts (5%) a month after sowing to spray 3 times at intervals of 15 days.
Irrigation
Garlic cultivation done by irrigation as well as rainfed cultivation. In irrigation cultivation, irrigation can be done at the time of planting and then, once in 3 days.
Cultivation methods after planting:
Weeds can be removed once in a month. Each time of weeding, to avoid from sun exposure of garlic, the covering of soil is necessary.
|
Crop Protection
Insects:
Thrips
-
Spray Neem oil 1 to 3 %.
-
Spray 10% Need seed juice 45, 60, 75th day after planting.
-
In 10 liters of water, add 300ml Dasakavya and 30 ml Nilgiri oil to spray 3 times for 15 days.
White Nematode
-
Summer tillage can be controlled the mother pests and cocoons.
-
Light traps can be fitted at night in April-May in the field.
-
In the morning hours to destroy the beetles by hand.
-
3rd stage larvae July- August months, taking the hand to destroy.
-
Metarizium anisopili 20 kg / ha to be applied when preparing to land at the scale.
Diseases
Smut disease
Agni hotra ash (200 g Agni hotra ashes mixed with 1 liter of cow urine after being held for 15 days dissolved in 10 liters of water and spray) a month after planting spray 3 times in a month interval.
Spray 3% Dasakavya solution for 3 times at 15 days interval.
Soil borne diseases:
Garlic rot disease
-
Trichoderma viride @ 5 kg / ha can be applied.
-
Pseudomonas florascens 5 kg / ha can be applied.
-
To control the disease Pseudomonas solution can be applied the root for 7 days.
-
Vermicompost 5 tons / ha to be applied when preparing to land at the scale.
|
 |
| Thrips Infested Garlic |
 |
| Garlic Clove Rot Disease |
|
-
5 tons of mushroom compost manure is to be applied. Also Phospobacteria, Azospirillum 5kg/ha with 50kg well decomposed farmyard manure can be applied while preparing the land.
-
Cowdug manure 75g/ha mix with 40 L water and make a solution and spray this solution while preparing the land.
Growth regulators
-
Panchgavya and dasakavya 3% solution is to spray 3 times for 15 days.
-
10 % vermicompost fertilizer a month after sowing Dithering to spray 3 times at intervals of 15 days.
-
Cow horn silica: 250 g / ha dissolved in 100 liters of water to spray for foliar application at the 65th day after planting.
-
Manchariyan tea extracts (5%) a month after sowing to spray 3 times at intervals of 15 days.
Irrigation
Garlic cultivation done by irrigation as well as rainfed cultivation. In irrigation cultivation, irrigation can be done at the time of planting and then, once in 3 days.
Cultivation methods after planting
Weeds can be removed once in a month. Each time of weeding, to avoid from sun exposure of garlic, the covering of soil is necessary. |
|
Rubber nature of Garlic
Nilgiris, Kodaikanal in Tamil Nadu, such mountain areas white garlic is cultivated in 500 hectares. For some years, the white garlic in these mountain areas, garlics without solid it like rubber ball such as compressibility, caused major loss on sale to farmers. In many cases, pre-harvest sprouting and garlic spread, so the quality will reduce and the farmers forced to sell at low prices too.
White Garlic does not reach the rubber nature by the fungus or germs, which can spread disease. Garlic cultivation done in the soil which can be containing more nutrients, applied high level of nitrogen fertilizers, particularly application of urea, high quantity of irrigation possible to improper growth of plant and result for garlic’s rubber nature. Garlic teeth does not attained soild besides the inside the teeth the production of vein leaves finally garlic obtained rubber nature.
Causes of rubber nature
-
White garlic rubber and teeth formation of garlic was due to the poor drainage facility in hilly zones and rainy seasons, in the areas of water stagnating and silty soil low lying areas.
-
Higher level watering also a cause for rubber nature.
-
Excess Nitrogen i.e, 150 to 250 kg applying is also produced large quantity of rubber garlic. Applying of High levels of nitrogen, urea increases the number of rubber garlic.
|
 |
| Rubber Garlic |
|
-
Excess nitrogen causes large number of rubber garlic as well as thrips attack the crop higher level. In consequence of injuries sustained leaves the "blast" fungal diseases attack the crop and to increase the number of rubber garlic incidence and reduced the yield.
-
In short term variety (Mettupalayam) affect higher-level rubber nature than long-term variety (Singapore).
-
There is large spacing in planting facilitate the crop to get nitrogen as well as water frequently. It increases the crop growth, because of these the garlic quality reduced.
|
Prevention methods of rubber nature
-
The farmers applied 2500 to 2700 kg / hectare number 4 and 5 mixed fertilizers more than the crop need, i.e., 150-250 kg Nitrogen, 225 to 300 Phosphorus and 150 to 200 kg Potassium. This exacerbated the impact. In contrast of natural fertilizers like farm yard manure 50 ton, vermin compost 5 ton, Bio compost manure 5 ton and mushroom compost manure 5 ton application to obtain a high yield, good quality and the garlic harvest.
-
Already potato, carrot, cabbage and vegetables grown in places, after harvest significant amounts of fertilizers in the soil before planting the white garlic soil test can be done and get recommendation of experts to study the best option.
-
If soil has over nitrogen, that time applying limited level of potassium will reduce the rubber nature and increase the garlic yield. With recommended natural fertilizers, the 30th day of crop planting apply 250 kg /ha of well burned ash will reduced the garlic sprouted in the field and increase the solid nature in garlic teeth.
-
In the short space of 15 cm row to row and 7.5 cm row spacing the garlic teeth planting should be done
-
Spray Boron 0.1% and Molybdenum 0.05% 45, 50, 75th day of planting will increase the garlic yield up to 18% and significantly the number of rubber garlic.
|
|
Harvesting:
The garlic plant leaves turn in to yellow colour, and then the leaves will dry up completely. At this stage pick the garlic bulbs with hands, should be accumulated. A size of 2 cm above the spines of garlic bulbs to be cut. After drying in the sun for two days, separate the quality depending on the size and weight.
Yields
10-15 ton / ha
For more details
Professor and Head
Horticultural Research Station
Vijayanagaram, Ooty - 643 001
Phone: 0423-2442170
email: hrsooty@tnau.ac.in |
|
|
|

