Deficiency Disease Of Vitamins
VITAMIN A: (Retinol)
The important deficiency states due to lack of vitamin A in the diet are:
i. Night Blindness: In the early stages of vitamin A deficiency, the individual cannot see well in dim light. In advanced deficiency, the subject cannot see objects in dim light.
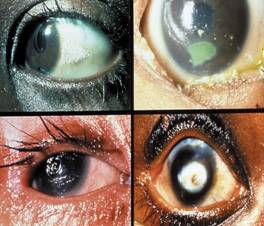
ii. Xerosis Conjunctiva: The conjunctiva is dry, thickened, wrinkled and pigmented. The pigmentation gives conjunctiva a smoky appearance.
iii. Xerosis Cornea: When dryness spreads to cornea, it takes on a hazy, lusterless appearance.
iv. Bitot’s Spots: Greyish glistening white plaques, formed of desquamated thickened conjuctival epithelium, usually triangular in shape and firmly adhering to the conjuctiva.
Under the national prophylaxis programme against nutritional blindness 2,00,000 IU of vitamin A in oil is administered every six months to preschool children to eliminate vitamin A deficiency.
SOURCES
In the animal foods, vitamin A is present in the form of retinol and its allied organic compounds, which are highly bioavailable. Though expensive, eggs are good sources of vitamin A and other nutrients and advocated as a measure to prevent vitamin A deficiency.
Over 80 per cent of the diary supply of vitamin A in the Indian diets is derived from its precursors, b-carotene, a-carotene, g-carotene and b-cryptoxanthin which are present in many plant foods. Among these carotenoids, b-carotene has the highest vitamin A activity. Green leafy vegetables and yellow orange fruits and vegetables like mango, papaya and carrots are rich source of b-carotene.
Vitamin A content of foods
| Name of the foodstuff |
Vitamin A mg/100g |
Liver sheep |
6690 |
Butter |
960 |
Hydrogenated oil |
750 |
Ghee (cow) |
600 |
Egg hen |
420 |
Whole milk powder (Cow’s milk) |
420 |
Chesse |
82 |
Buffalo’s milk |
53 |
Curds, cow’s milk |
31 |
Mutton |
9 |
TREATMENT
Immediately on diagnosis, an oral dose of 200,000 IU of oil miscible vitamin A should be given to children in the age group of 1-6 years. In the case of those with persistent vomiting and diarrhoea an intramuscularly injection of 1,00,000 IU of water miscible vitamin A can be substituted for the oral dose.
This is followed by another dose of 2,00,000 IU one to four weeks later. In the case of infants and children weighing less than 8 kg, the schedule may be followed using half the dose of vitamin A. Acute corneal lesions should be considered as medical emergency and should be referred to the nearest hospital for treatment of the general condition in addition to the treatment of the eye disease.
Treatment Schedules for Xerophthalmia–Oil Miscible oral Vitamin A
|
< 1 year of age |
> 1 year of age |
Immediately |
100,000 IU |
200,000 IU |
Next Day |
100,000 IU |
200,000 IU |
2-4 weeks later |
100,000 IU |
200,000 IU |
Severe Protein Energy Malnutrition (PEM) |
|
|
Additional monthly dose until PEM resolves |
|
|
Source : WHO / UNICEF / VACG Task Force, 1988.
VITAMIN D (7 - DEHYDRO CHOLESTROL)
The chief signs in fully developed active rickets are found in the chest wall (beading), waists and ankles (thickening) and various deformities (knock - knees and bow legs). The child is restless, fretful and pale with flabby and toneless muscles, which allow the limbs to assume unnatural postures. Development is delayed so thatthe teeth often erupt late and there is failure to sit up, stand, crawl and walk at the normal ages. There is usually a protuberant abdomen so called potbelly.
ii. OSTEOMALACIA
It may be called as adult rickets. It occurs generally in pregnant women. The changes in bone are similar to rickets. Skeletal pain is usually present and persistent and ranges from a dull ache to severe pain. Muscular weakness is often present and the patient may find difficulty in climbing stairs or getting out of a chair.
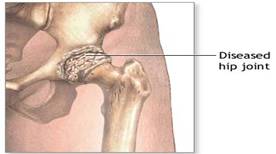
The differential diagnosis of osteomalacia and osteoporosis
Features |
Osteomalacia |
Osteoporosis |
General |
|
|
Type |
It is a deficiency disease |
It is not a primary deficiency |
Age at which it occurs |
It occurs in the reproductive stage due to repeated pregnancies |
It occurs in the post menopausal stage |
Composition of bone |
Composition of bone changes. Amount of calcium and phosphorous is low and bone become translucent |
Composition of bone remains the same. Decrease in quantity of the bone |
Deficiency |
Less accretion of calcium and phosphorous in the bone due to the deficiency of vitamin D |
Resorption of the bone is more due to the deficiency of estrogen. |
Sex |
It occurs mostly in women |
It occurs mostly in women but men can also get it. |
Clinical features |
|
|
Skeletal pain |
A major complaint usually persistent |
Episodic and usually associated with a fracture |
Muscle weakness |
Usually present and producing disability and when severe, a characteristic gait. |
Absent |
Fractures |
Relatively uncommon; healing delayed |
The usual presenting feature; heals normally |
Skeletal deformity |
Common, especially kyphosis |
Only occurs where there is a fracture |
Radiographic features |
|
|
Loss of density of bone |
Widespread |
Irregular and often most marked in the spine |
Looser’s Zones (Rarefaction of bone and Translucent bands) |
Diagnostic |
Absent |
Biopsy |
|
|
Histological changes |
Excess osteoid tissue with bone present in normal quantity |
Bone reduced in quantity but fully mineralized |
Biochemical changes |
|
|
Plasma Ca and P |
Often low |
Normal |
Plasma alkaline phosphatase |
Often high |
Normal |
Urinary calcium |
Often low |
Normal or high |
Response to treatment |
|
|
Vitamin D |
Dramatic |
None |
Source : (Modified) Passmore, R and M.A. Eastwood, 1990, Davidson and Passmore, Human nutrition and Dietetics, Modified ELBS, Churchill Livingstone.
In prescribing medicinal vitamin D under certain situations where there is minimal exposure to sunlight, a specific recommendation of a daily supplement of 400 mg is made by ICMR.
Vitamin D is now considered more as a prohormone than a vitamin. It can be synthesized in the body in adequate amounts by simple exposure to sunlight.
SOURCES
Most foods have negligible amounts of vitamin D. certain marine fishes are known to be good sources of vitamin D. Egg yolk, butte and milk have some vitamin D and can be considered as poor sources. Recent work indicated that even the fresh water fishes have moderate amounts of vitamin D3 in liver.
Vitamin D content of foods
Name of the foodstuff |
Vitamin D IU/100g |
Cod liver oil |
10,0000 |
Shrimp |
150 |
Liver (Lamb) |
120 |
Mackerel |
120 |
Cod |
85 |
Butter |
35 |
Egg yolk |
25 |
Beef steak |
13 |
Cheese |
12 |
Corn oil |
9 |
Milk (cow) |
03-4.0 |
Beet greens |
0.2 |
Spinach |
0.2 |
Cabbage |
0.2 |
Source: Guthrie Helen, A. and Mary Frances Picciano, 1999, Human Nutrition, WCB McGraw Hill, Boston.
TREATMENT
A daily oral dose of 25-125 mg (1000-500 IU) of vitamin D cures rickets and osteomalacia. Because of the risk of toxicity this should be reduced to 10 mg, the prophylactic dose, when plasma alkaline phosphatase has returned to normal and radiographs show that healing is established. Children can be given 1 ml halibut oil.
Advice on diet and general hygiene is needed. An adequate intake of calcium is essential. The best source is milk and at least 500 ml should be taken daily. An egg daily and butter or fortified margarine to increase the dietary intake of vitamin D are recommended. Children should enjoy playing in the sun.
VITAMIN E (TOCOPHEROL)
Vitamin E deficiency in animals causes several disorders such as reproduction failure, liver necrosis, etc,
SOURCES
Vegetable oils, nuts and whole grams are the richest natural sources of vitamin E (wheat germ oil contains 120 mg/100 g oil) Rice bran oil contains a high amount of unsaponifiable compounds such as tocotrienols and oryzanol which have antioxidant activity. It is present in small quantities in lettuce, grasses and embryos of many seeds. In general plant foods are richer sources of vitamin E than animal foods.
Vitamin E content of vegetable oils is found to be higher than many other foodstuffs. Prior heating of the oil is a common method used for many of our food preparations. It is seen from Table that oils when heated to their smoking points lost appreciable amounts of tocopherols; this loss correspondingly increased with the length of duration heating. When the oils are oxidized in the presence of air, peroxides are formed and tocopherols are destroyed.
Vitamin E content of foods
| Name of the foodstuff |
Vitamin E mg% |
| Wheat flour |
6.5 |
| Bajra flour |
8.8 |
| Jowar flour |
2.2 |
| Maize flour |
6.2 |
| Rice flakes |
3.4 |
| Rice |
3.7 |
| Red gram dhal |
10.2 |
| Green gram whole |
12.4 |
| Moth beans |
10.0 |
| Onion |
1.1 |
| Yam |
3.2 |
| Cluster beans |
11.6 |
| French beans |
8.3 |
| Cauliflower |
6.8 |
| Butter |
5.1 |
| Ghee |
2.8 |
| Vanaspati |
6.7 |
| Mustard oil |
86.2 |
| Groundnut oil |
35.9 |
| Sesame oil |
53.1 |
Sources : Gupta Soame and B.D. Punekar, 1978. Studies on vitamin E content of commonly consumed food stuffs and influence of heating vegetable oils. S.N.D.T. University, Bombay.
In general, length and conditions of storage affect the vitamin E content of a foodstuff to a great extent.
VITAMIN K
Vitamin K deficiency leads to haemorrhagic conditions.
SOURCES
The concentration of vitamin K in foods is highest in dark green leafy vegetables but is also found in fruits, tubers, seeds and dairy and meat products. Vitamin K usually occurs in association with chlorophyll in the chloroplases of plants. Alfalfa is a specially rich source. The average diet provides enough vitamin K hence there is no need for a supplement.
VITAMIN C (ASCORBIC ACID) Severe Vitamin C deficiency results in the development of the disease scurvy. The disease is characterized by
a) General weakness followed by shortness of breath, pain in bones, joints and muscles of the extremities.
b) Swollen and tender joints, haemorrhages in various tissues and pain in joints.
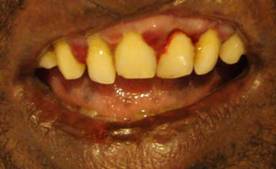
c) Bleeding gums and loose teeth.
In infantile scurvy, the infant screams if picked up or moved or handled. There is pain and tenderness of the limbs.
VITAMIN B1 (THIAMINE)
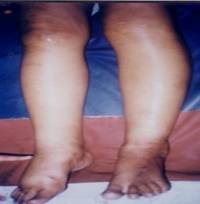
Thiamine deficiency causes the disease, beriberi, in human beings. Two forms of beriberi namely wet beriberi and dry beriberi occurs in adults. The first symptoms are anorexia (loss of appetite) with heaviness and weakness of the legs. There is pain and numbness in the legs. The subjects feel weak and get easily exhausted. Oedema is the important feature of wet beriberi. The calf muscles are swollen. The pulse is fast and bouncing. The heart becomes weak and death occurs due to heart failure. In infantile beriberi, the first symptoms are restlessness, sleeplessness and cardiac failure.
VITAMIN B2 OR RIBOFLAVIN
Riboflavin deficiency is characterized by
a) ANGULAR STOMATITIS
The lesions at the angles of the mouth are termed as angular stomatitis.
The tongue in general is acutely inflamed called as glossitis.
c) Skin lesions occur on the nasolabial folds and on the ears
d) Cheilosis which is the dry chapped appearance of the lips.
e) Behavioural abnormalities occur in riboflavin deficient children.
VITAMIN B3 (NIACIN)
Niacin deficiency causes the disease pellagra in humans. Pellagra is also called Disease of 3D’s. Because the disease has the symptoms of diarrhoea, dermatitis and depression. The disease is characterized by the following.
a)GLOSSITIS AND DIAHHOREA - These are the two outstanding symptoms. Nausea and vomiting are seen in most cases.
b) The DERMATITIS is the most characteristic symptom of the disease. The commonest sites are the back of the fingers and hands, the forearms, and the neck.

b) GLOSSITIS
Milder mental disturbances consisting of irritability, depression, inability to concentrate and poor memory are common in niacin deficiency.
VITAMIN B6 OR PYRIDOXINE
Pyridoxine deficiency results in the following
a) Hypochromic microcytic anaemia.
b) Sleep disturbances, irritability and depression
c) Angular stomatitis, glossitis and cheilosis in pregnant and lactating mothers.
PANTOTHENIC ACID
The visible signs of deficiency include nausea, vomiting, tremor of the outstretched hands, irritability and burning feet syndrome.
FOLIC ACID
Folic acid deficiency causes megaloblastic anaemia mainly in pregnant women of low income groups.
VITAMIN B12
Vitamin B12 deficiency causes perinicious anemia in humans. Soreness and inflammation of the tongue are commonly observed. Parasthesia (numbness and tingling) occurs in fingers and toes. Persons living exclusively on vegetarian diets develop vitamin B12 deficiency.
Source
http://www.textbooksonline.tn.nic.in/Books/12/HomeSci-EM/Chapter-3.pdf
http://images.google.co.in/imgres?imgurl=http://www.cehjournal.org/images/ceh_14_40_072_f01.jpg
http://lh5.ggpht.com/pellagra.jpg |





