Introduction :
Antioxidants are naturally occurring chemicals in foods that help to counter the detrimental effects of oxygen free radicals, which form during normal metabolism and through external factors such as x-rays, ultra-violet radiation and pollution. Antioxidants are phytochemicals, vitamins and other nutrients that help to protect our cells from FREE RADICALS. Antioxidants are absolutely critical for maintaining optimal cellular and systemic health and well-being. They are nature's way of fighting off potentially dangerous molecules in the body.
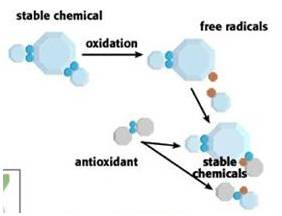
Free radical molecules are missing one or more electrons, and this missing electron is responsible for biological oxidation. The incomplete molecules aggressively attack other molecules in order to replace their missing parts. These reactions are called "oxidation" reactions. To balance out these unruly molecules, the body also creates antioxidants, which have the sole purpose of neutralizing free radicals.
Free radicals are harmful molecules that can cause damage or death to cells in the body. Every day tens of thousands of free radicals are generated within the body, causing cell damage that can lead to chronic and degenerative diseases if left unchecked. The body sometimes creates its own free radicals in order to destroy viruses or bacteria. The role of antioxidants is to neutralize, or “stop,” free radicals from doing damage to your body.
|
 |
The following is a list of different kinds of antioxidants and foods that are high in each.
Antioxidants |
Foods |
| Allium sulphur compounds |
Leeks, onions, garlic |
| Anthocyanins |
Eggplant, grapes, berries |
| Beta carotene |
Pumpkin, mangoes, apricots, carrots, spinach, parsley |
| Catechins |
Red wine, tea |
| Copper |
Seafood, lean meat, milk, nuts, legumes |
| Cryptoxanthins |
Red peppers, pumpkin, mangoes |
| Flavonoids |
Tea, green tea, red wine, citrus fruits, onion, apples |
| Indoles |
Cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower |
| Lignans |
Sesame seeds, bran, whole grains, vegetables |
| Lutein |
Corn, leafy greens (such as spinach |
| Lycopene |
Tomatoes, pink grapefruit, watermelon |
| Manganese |
Seafood, lean meat, milk, nuts |
| Polyphenols |
Thyme, oregano |
| Selenium |
Seafood, offal, lean meat, whole grains |
| Vitamin C |
Oranges, berries, kiwi fruit, mangoes, broccoli, spinach, peppers |
| Vitamin E |
Vegetable oils, nuts, avocados, seeds, whole grains |
| Zinc |
Seafood, lean meat, milk, nuts |
| Zoochemicals |
Red meat, offal, fish |
 |
 |
Important benefits of antioxidants include:
Repairing damaged molecules: Some unique types of antioxidants can repair damaged molecules by donating a hydrogen atom. This is very important when the molecule is a critical one, like your DNA
Blocking metal radical production: Some antioxidants have a chelating effect – they can grab toxic metals like mercury and arsenic, which can cause free radical formation, and "hug" them so strongly to prevent any chemical reaction from taking place. Water-soluble chelating agents can also escort toxic metals out of your body through your urine.
Stimulating gene expression and endogenous antioxidant production: Some antioxidants can stimulate your body's genes and increase your natural defenses.
Providing a "shield effect": Antioxidants, such as flavonoids, can act as a virtual shield by attaching to your DNA to protect it from free radicals attacks.
Promoting cancer cells to "commit suicide": Some antioxidants can provide anti-cancer chemicals that halt cancer growth and force some cancer cells to self-destruct (apoptosis).
Other benefits of eating antioxidant rich foods
- Support kidney function
- Improve reproductive function
- Maintain good dental health
- Have anti-ageing effect- Apricots, Cantaloupe, Lemon, Pecans, Almonds, Sunflower seeds
- Improve nervous system functioning
- Support the immune system & improve defence power of the body
- Protect the liver
- Reduce obesity
- Maintain healthy vision
- Offer protection against digestive disorder
- Improve quality of sleep
- Support respiratory system
- Fights against cholesterol – Beans
- They fight against cancer – Cranberry, Raspberry, Pomegranate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
SOURCE :
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antioxidant
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/antioxidants.html
http://www.mydr.com.au/nutrition-weight/antioxidants-their-role-in-health
http://www.powerhealth.gr/en/antioxidants/
|
|

