Egg
Hen’s egg consists of three main parts, the shell, the egg white and the egg yolk. The shell consists of calcite crystals embedded in a matrix of proteins and polysachharide complex. Inside the shell the viscous colourless liquid called the egg white accounts for about 60 per cent of the total egg weight. Eggs have high nutritional value. moreover egg, eggs may be used as thickening agents, binding and coagulating agents, coatings, foaming agents, emulsifiers, shortening agents, flavouring agents and colorant in a variety of food products.
COMPOSITION OF EGG
Percentage distribution of weight
| Part |
Weight % |
| Shell |
8-11 |
| White |
56-61 |
| Yolk |
27-32 |
Percentage composition of egg white and yolk
Nutrients |
Egg white |
Egg yolk |
| Water |
88.0 |
48.0 |
| Protein |
11.0 |
17.5 |
| Fat |
0.2 |
32.5 |
| Minerals |
0.8 |
2.0 |
Egg white is composed of thin and thick portions. 20-25% of the total white of fresh eggs (1-5 days old) is thin white. The chief constituents of egg white besides water are proteins. Different types of proteins are present in egg white.
Ovalbumin
This constitutes 55% of the proteins of egg white. This is a phospho glycoprotein and is composed of three components A1, A2, and A3, which differ only in phosphorus content.
Conalbumin
This constitutes 13% protein of the egg albumin. It consists of two forms neither of which contains phosphorus nor sulphur.
Ovamucoid
It is a glycoprotein. This constitutes about 10% of the egg white proteins.
Ovomucin
This protein is responsible for the jelly like character of egg white and the thickness of he albumin. It contains 2% of the egg white. Its content in he thick layers of albumin is about 4 times more than in thin layers. It is insoluble in water but soluble in dilute salt solution.
Lysozyme
3.5% of the egg white protein is lysozyme. This is an enzyme capable of lysing or dissolving the cell of wall of bacteria. It is composed of 3 components A, B and C. It binds biotin and makes the vitamin unavailable.
Avidin
Avidin is 0.05% of the egg white protein. It is denatured by heat and cooked eggs do not affect the availability of biotin.
Ovoglobulin
It is a protein consisting of two components G1 and G2 and both are excellent foaming agents.
Ovoinhibitor
0.1% of egg protein is made up of ovoinhibitor. It is another protein capable of inhibiting trypsin and chymotrypsin.
Egg yolk
 Solid content of yolk is about 50%. Solid content of yolk is about 50%.
Percentage composition of egg yolk on dry weight basis
Nutrient |
Granules |
Plasma |
| Lipid |
34 |
77-81 |
| Protein |
60 |
18 |
| Ash |
66 |
2 |
The major proteins in egg yolk are lipoproteins, which include lipovitellins and lipovitellinin. The lipoproteins are responsible for the excellent emulsifying properties of egg yolk, when it is used in such products as mayonnaise.
Fatty acid composition of egg yolk
Fatty Acid |
% of total
fatty acids |
| C16:0 Palmitic acid |
23.5 |
| C18:0 Stearic acid |
14.0 |
| C18:1 Oleic acid |
38.4 |
| C18:2 Linoleic acid |
16.4 |
| C18:3 Linolenic acid |
1.4 |
| C18:4 Arachidonic acid |
1.3 |
NUTRITIVE VALUE OF EGG /100 g
| Nutrient |
Amount |
Nutrient |
Amount |
| Energy (K cal) |
173.0 |
Carotene (µ/g) |
600 * |
| Protein (g) |
13.3 |
Thiamine (mg) |
0.1 |
| Fat (g) |
13.3 |
Riboflavin (mg) |
0.4 |
| Calcium (mg) |
60.0 |
Niacin (mg) |
0.1 |
| Phosphorus (mg) |
220.0 |
Folic acid (µ/g) |
78.3 |
| Iron (mg) |
2.1 |
|
|
* +360 mg of vitamin A
EVALUATION OF EGG QUALITY
The quality of the egg in the shell is evaluated by candling. The egg is held up to an opening behind which is a source of strong light. Candling will reveal
A crack in the shell.
The size of the air cell.
The firmness of albumin.
The position and mobility of yolk and
The possible presence of foreign substances like blood spots, moulds and developing embryo.
If the egg sinks it is considered as good. Poor quality egg floats (due to increase in air cell). It shows that the egg floating in water has lost in weight due to dehydration.
Good quality egg has 72 haugh units and as the quality deteriorates it comes down to 36-60.
The height of the thickest portion of the white is divided by the diameter of the egg gives white index.
Measurement of the height of the yolk in relation to the width of the yolk gives the yolk index.
The interior quality of the egg deteriorates from the time it is said to until it is consumed. With proper care, however, this decline in quality can be minimised.
Fertile eggs get deteriorated more rapidly than infertile eggs. Deterioration takes place as physical and chemical changes takes place.
Egg white becomes less viscous and spreads rapidly.
The size of the air cell and volume increases.
Loss of water, carbon dioxide, protein break down, egg flavour deteriorates.
Bacterial decomposition takes place.
Upon heating the egg proteins are denatured and then gradually aggregate to form a three-dimensional get network. Ovalbumin the main protein in egg white is a globular protein denatured by heat. The range in temperatures over which coagulation takes place varies with the rate of heating. Heating on egg much beyond this temperature shrinks and toughens the coagulum of the white.
PRESERVATION OF EGGS
Egg breaking, separation and pasteurization and freezing are the steps involved. whole egg or yolk, in contrast, can be pasteurized at 60 – 61.5 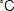 for 3.5 -4.0 minutes., without significant changes in physical and functional properties. the pasteurized whole or separated eggs are placed in cans or suitable container and frozen in sharp freezer room with circulating air at -29 for 3.5 -4.0 minutes., without significant changes in physical and functional properties. the pasteurized whole or separated eggs are placed in cans or suitable container and frozen in sharp freezer room with circulating air at -29 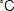 . freezing may take from about 48 to 72 hours. Eggs are pasteurized to kill all Salmonella organisms. . freezing may take from about 48 to 72 hours. Eggs are pasteurized to kill all Salmonella organisms.
Eggs are usually stored at –1.5 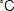 to 0 to 0 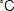 which is just above their freezing point. Only eggs of high quality should be stored. They remain in desirable condition only if the storage room is well controlled as to humidity, 85-90% circulation of air and free from objectionable odours. Eggs may retain quality as long as 6 months in cold storage. Before being placed in cold storage, eggs may be dipped in light mineral oil. which is just above their freezing point. Only eggs of high quality should be stored. They remain in desirable condition only if the storage room is well controlled as to humidity, 85-90% circulation of air and free from objectionable odours. Eggs may retain quality as long as 6 months in cold storage. Before being placed in cold storage, eggs may be dipped in light mineral oil.
It is a satisfactory method for preserving eggs, either whole or as separated yolks or whites. Spray dried egg white and egg yolk has long shelf life.
VALUE ADDITION OF EGG
SOURCE
www.indiaagronet.com
bhawanalovescooking.blogspot.com/2008/02/suga.. |

 Solid content of yolk is about 50%.
Solid content of yolk is about 50%.