Cocoa and chocolate are made by grinding the seeds of the pods of the cacao tree (Theobroma cacao) which is indigenous to Central America and is grown extensively in Brazil, West Indies and Srilanka. Cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) a native of Amazon base of South America got its entry into India in the early half of the 20th century. Administratively it is conferred plantation status like coffee, tea and rubber but is seldom recognized as a plantation crop under the Indian Agrarian Administrative Sector. It is also one of the supporter of Agro-based industry in India. Cocoa beans are the primary raw material for confectioneries, beverages, chocolates and other edible products. The commercial sector of cocoa in India hardly takes place in a major way in the international export trade. Majority of the processed cocoa products are consumed within India. The tropical diversified congenial climate available in India provides immense scope for its cultivation.
1. Fermentation
Fermentation of Cocoa beans is essential to remove the mucilaginous pulp, to develop flavour and aroma precursors, reduce bitterness, kill the germ of the seed and to loosen the testa. Among the various methods adopted for fermentation in different cocoa producing countries, Heap, Box Tray and Basket methods are considered as the standard methods.
2. Heap Method
This method involves keeping a mass of not less than 50 kg of wet beans over a layer of banana leaves. The banana leaves are spread over a few sticks to keep them a little raised over the ground level to facilitate the flow of sweating. The leaves are folded and kept over a heap of beans and a few wooden pieces kept over it to keep the leaves in position. The heaps are dismantled and the beans mixed the third and fifth days. It needs about six days for the completion of fermentation and the beans can be taken out for drying on the seventh day.
Even though the minimum quantity of beans required for effective fermentation is 50 kg. a further increase in quantity of beans in a heap will be beneficial. However, heaps of more than about 500 kg. May be difficult to handle.
3. Tray Method
Wooden trays of size 90 cm x 60 cm x 13 cm with battens or reapers fixed at the bottom with gaps in between, are filled with beans. Each tray can contain about 45 kg. wet beans. Six such trays are stacked one over the other and an empty tray is kept at the bottom to allow for drainage of sweating. After stacking, the beans of the top most tray are kept covered with banana leaves.
After 24 hours of setting the stack of trays is kept covered with gunny sacking to conserve the heat that develops. There is no need for mixing the beans and fermentation will be completed in four days. On the fifth day the beans can be taken out for drying.
The minimum number of trays required to be stacked is about six but as many as 12 trays can be used simultaneously.
4. Box Method
Wooden boxes of 1.2 x 0.95 m x 0.75 m with holes at the bottom and sides of the box are filled with wet beans. These boxes can hold one M.T. of wet beans. The beans are to be mixed on alternate days. As the quantity of beans is high, this is best done by changing the beans from one box to another at the time of mixing. This would necessitate having a minimum of three boxes.
Wet beans taken for fermentation should be sufficiently ripe so as to separate the beans form the polacuta and husk easily. Minimum quantity of wet beans for a normal fermentation is about 100 kg. The duration of fermentation is commonly for 3-5 days i.e., 72-120 hrs. Fermentation over 120 hours will cause loss of chocolate flavour and development of off flavour.
5. Drying and Storage
The fermented beans can be dried either in the sun or by artificial means. Sun drying can be done in thin layers of 2 - 3 cm. depth and stirring from time to time. When the beans are dried properly, they produce a characteristic cracking sound on compressing a fistful of beans in the palm. The more scientific method is to use moisture meter. The dried beans after cooling maintaining 6 -8% moisture should be cleared before storage. The fruit broken, shriveled and other extraneous materials are removed. The cleared bags are kept on a raised platform of wooden planks.
6. Roasting
Roasting develops characteristic flavour and colour. It also causes change in the chemical structure of polyphenols producing less astringency compounds. The roasting also changes the colour to dark brown.
7. Grinding and Defatting
The roasted beans are cooled and gently crushed soon after, to fracture the husk and break down the kernels into their natural angular fragment or nibs. The roasted nibs are ground using stone mills to a fine paste or liquor. The heat produced during grinding causes the cacao fat to melt.
Percentage nutritive value of cocoa and chocolate
Constituents |
Cocoa |
Chocolate |
Water |
4.6 |
5.9 |
Protein |
21.6 |
12.9 |
Fat |
28.6 |
48.7 |
Carbohydrate |
37.7 |
30.0 |
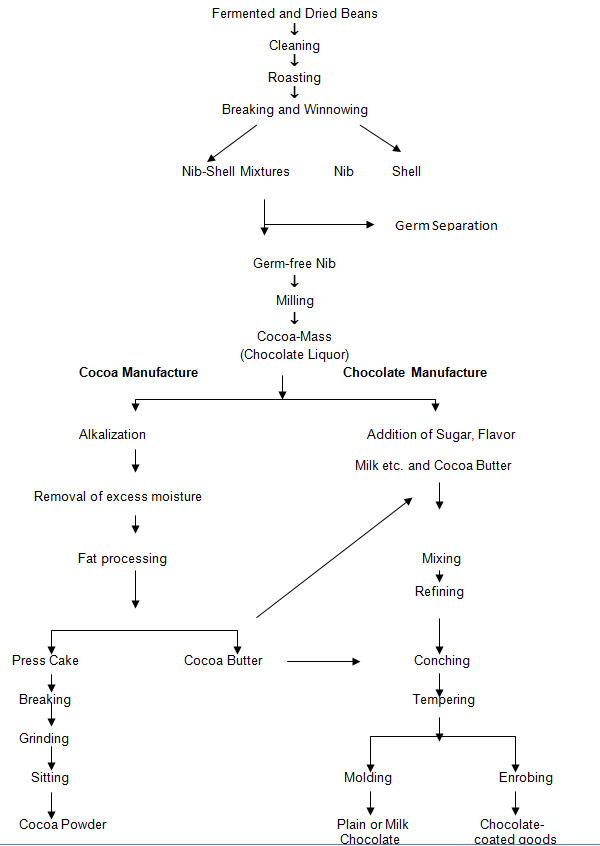
FLOWCHART FOR COCOA AND CHOCOLATE MANUFACTURING *

FUDGE **
Fudge is generally prepared from brown sugar. As brown sugar contains a higher percentage of invert sugar than white sugar, sucrose crystallizes less readily. Fudge ripens during storage and becomes soft and velvetty after 24 hr storage.
Ingredients
Sugar |
200 g |
| Milk |
120 g |
| Butter |
14 g |
| Chocolate |
21 g |
Procedure
-
Add the chocolate and butter to cooking pan and heat it on a steam bath till the chocolate and butter have melted add sugar. Mix the chocolate and butter well with sugar.
-
Then add milk and heat till the sugar dissolves completely
-
Cook the syrup to a soft ball stage (112 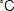 )
-
Allow it to cool to about 70 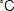 and transfer to a greased moulding pan
-
Cut the candy when it is cool and wrap in butter or foil and store in an air-tight container.
TECHNOLOGIES AVAILABLE
* - Post Harvest technology Centre, TNAU, Coimbatore.
** - Home Science College and Research Institute, TNAU, Madurai.
SOURCE
-
http://graph.exportpages.com/ppic/P73240F19470.jpg
-
http://ar030.k12.sd.us/Chocolate.png
|





