Coffee
Coffee is an important beverage used all over the world.

Processing procedure
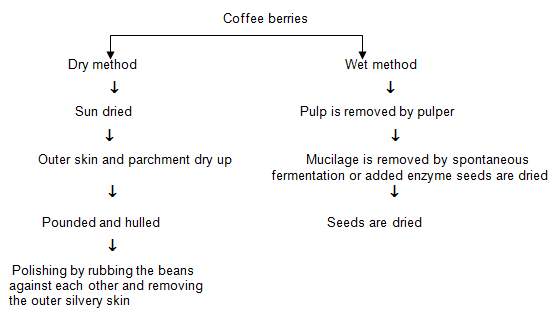
Coffee processing consists of removing the skin, pulp, parchment and silver screen. The quality of the final product depends upon the manner of processing. It is the curing process that prepares the coffee beans for market. Two methods are employed for processing- the dry and wet. In the dry method the beans are sun dried. In the wet method, known as the washed coffee process, pectin enzymes are used on selectively picked cherries to replace spontaneous fermentation.
Coffee curing process
Cured coffee is graded according to sizes and shapes. The different plantation grades are:
-
Pea berry (oval shaped beans)
-
or A (first size in flats- bold, heavy and well formed)
-
B (slightly smaller than O or A)
-
C (slightly smaller than B)
-
Triage (pale, discoloured, black spotted beans including bits)
The manufacture of coffee powder involves roasting, grinding, blending and packing.
Roasting
During roasting many physical and chemical changes occur, which develops pleasant aroma, flavour, brown colour and good taste.
Grinding
Roasted beans are ground to three sizes, namely, fine, medium and coarse. Coarse ground powder retains aroma and flavour better and longer than fine ground powder. Coarse ground powder is more suitable for preparing coffee decoction by percolation.
Blending
Two types of coffee powder are marketed namely pure coffee prepared from coffee beans only and French coffee containing chicory. The proportion of chicory should not exceed 50%. Strength, flavour, aroma and acidity are the chief criteria in judging the quality of coffee and judicious blending of different grades brings out these qualities ot the best advantage.
Coffee beverage

Coffee has no food value. The constituents that are of chief significance in the making of the beverage are caffeine, flavour substances and bitter substances. Several factors like water, temperature, material from which pot is made, agitation affects the quality of coffee.
Caffeine
It is an alkaloid substance producing the stimulating property. The longer the brewing time of coffee the more is caffeine extracted. It can be removed chemically from the bean to produce decaffeinated coffee.
Flavour
It is the sulphur compounds that are the main contributors to the flavour. The flavour substances are volatile.
Bitter substances
Polyphenol substances or tannins are hot water soluble. Hence longer the coffee is brewed, the greater will be the tannin content and the bitterness becomes pronounced.
Methods of coffee
Method |
Flavour |
Tannins |
Limitations |
| Filtration |
Retains well |
Extracts less |
Decoction may
not be hot |
Vacuum
coffee maker |
Retains well |
Extraction is more due
to the contact wit h the grounds at a high
temperature for few minutes. |
More bitter |
| Percolator |
Loss of flavour due to
constant aeration of
the brew as the liquid is forced up and sprayed the grounds |
Extraction is more due
to recirculation of hot water through the
coffee grounds |
More bitter |
| Steeping |
Retains best |
Extracts less |
Extraction of
flavour may not
be complete |
Coffee products
Soluble coffee
 Soluble coffee is a dried powdered water soluble solid made from very strong coffee brew. It is marketed as instant and is freeze dried coffee. Soluble coffee is a dried powdered water soluble solid made from very strong coffee brew. It is marketed as instant and is freeze dried coffee.
Iced coffee
A sparkling iced beverage that possesses that maximum amount of flavour is made by pouring a freshly made strong coffee infusion over crushed ice in a glass.
Coffee tablets
Coffee is also marketed in the form of tablets. Ground coffee is mixed with chicory powder and the mixture pressed in a machine after the addition of a binding material such as glucose.
Decaffeinated coffee
By a chemical process most of the caffeine can be removed from the beans to give decaffeinated coffee which has good flavour.
Source
capturetheimagination.wordpress.com/.../
www.tomscoffeehouse.com/main.asp?sec=blog...
http://img.photobucket.com/albums/v305/Atthevanguard/coffee.jpg
|




 Soluble coffee is a dried powdered water soluble solid made from very strong coffee brew. It is marketed as instant and is freeze dried coffee.
Soluble coffee is a dried powdered water soluble solid made from very strong coffee brew. It is marketed as instant and is freeze dried coffee.