|

I. SEASON AND VARIETIES
SEASON STRAIN
1. Adipattam (July - August) CO 1, COH (M) 4, COBC 1
2. Purattasipattam (September -October) CO 1, COH (M) 4, COBC 1
3. Thaipattam (January -February) CO 1, COH (M) 4, COBC 1
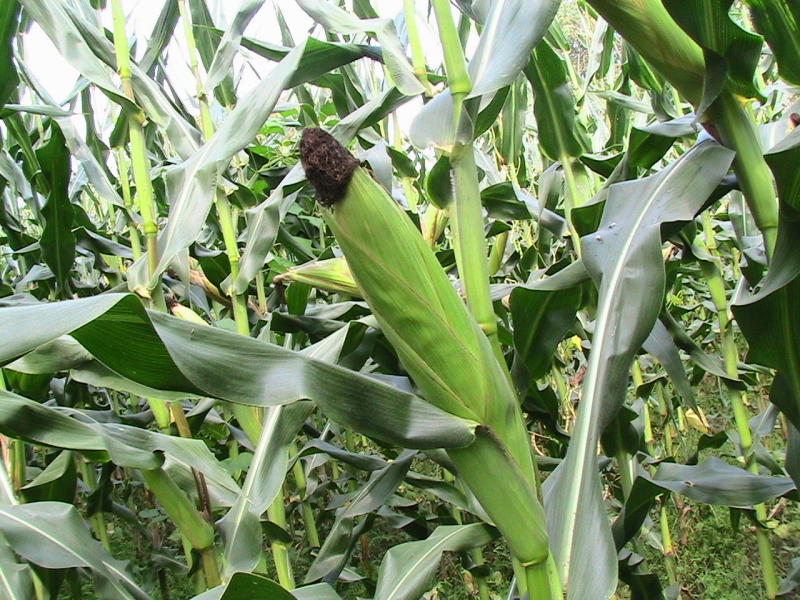
MAIZE - MORPHOLOGICAL DESCRIPTION
PARTICULARS |
CO 1 |
COH(M) 4 |
COBC 1 |
Parentage |
Unit Selection from Indonesian popu lation Suwan 1 |
(UMI 90 x xUMI 285) x UMI 112 |
Composite involving UMI 836 and UMI 836-1-2 |
Duration (days) |
105 - 110 |
94 (90 – 95 days) |
55 - 65
(fresh cobs harvest) |
Area of Adoption |
Coimbatore, Erode, Tirunelveli, Tanjore and Pudukottai |
Coimbatore, Dindugul, Erode, Salem, Virudhunagar, Perambalur, Tuticorin, Madurai and Theni districts |
All maize growing areas |
Rainfed/Irrigated |
Both |
Both |
Both |
Grain yield (kg/ha) |
|
|
|
Irrigated |
5200 |
5694 |
6.7 tonnes of tender cobs & 32.3 tonnes of green fodder / ha |
Rainfed |
3300 |
4521 |
3 tonnes of tender cobs per ha. |
Special features |
Resistant to downy mildew |
Shorter duration, suitable for rainfed areas |
2 to 3 cobs / plant, possessing delightful sweet taste and flavour |
|
Orange flint grains |
Moderate resistance to downy mildew and stemborer |
Suitable for inland and export market
Green fodder has good forage value |
Sheath colour |
Green |
Green |
Green |
Node colour |
Green |
Green |
Green |
Mid rib |
White |
White |
White |
Cob size |
Big |
Big |
Small |
Husk coverage |
Full |
Full |
Nil |
Grain colour |
Deep orange |
Yellow |
Yellow |
Nature of kernels |
Flint |
Flint |
Dent |

Maize - HYBRID COH (M) Maize - HYBRID COH (M)

Source: www.resimao.org
CROP MANAGEMENT
I. IRRIGATED MAIZE
1. APPLICATION OF FYM OR COMPOST
Spread 12.5 t/ha of FYM or compost or composted coir pith evenly on the unploughed field along with 10 packets of Azospirillum (2000 g/ha) and incorporate in the soil.
2. FIELD PREPARATION
Plough the field with disc plough once followed by cultivator ploughing twice, after spreading FYM or compost till a fine tilth is obtained.
3. FORMING RIDGES AND FURROWS OR BEDS
- Form ridges and furrows providing sufficient irrigation channels. The ridges should be 6 m long and 60 cm apart.
- If ridges and furrows are not made, form beds of size 10 m2 or 20 m2 depending on the availability of water.
- Use a bund former or ridge plough to economise cost of production.


4. APPLICATION OF FERTILIZERS
i. Apply NPK fertilizers as per soil test recommendation as far as possible. If soil test recommendation is not available adopt a blanket recommendation of 135:62.5:50 NPK kg/ha.
ii. Apply quarter of the dose of N; full dose of P2O and K2O basally before sowing.
iii. In the case of ridge planted crop, open a furrow 6 cm deep on the side of the ridge, at two thirds the distance from the top of the ridge.
iv. Apply the fertilizer mixture along the furrows evenly and cover to a depth of 4 cm with soil.
v. If bed system of planting is followed, open furrows 6 cm deep at a distance of 60 cm apart.
vi. Place the fertilizer mixture along the furrows evenly and cover to a depth of 4 cm with soil.
- When Azospirillum is used as seed and soil application, apply 100 kg of N/ha (25% reduction on the total N recommended by soil test).
Deficiency symptoms
Nitrogen deficiency |
: |
Leaves become yellow, older leaves show drying at the tips which progress along mid veins, stalks become slender. |
Phosphorus deficiency |
: |
Leaves are purplish green during early growth. Growth spindly, slow maturity, irregular ear formation. |
Potassium deficiency |
: |
Leaves show yellow or yellowish green streaks, become corrugated. Tips and marginal scorch. Tips end in ears are poorly filled. Stalks have short internode. Plants become weak and may fall down. |
Magnesium deficiency |
: |
Older leaves are the first to become chlorotic at margins and between veins. Streaked appearance of leaves. Necrotic or chlorotic spots seen in leaves. |
Zinc deficiency |
: |
Older leaves have yellow streaks or chlorotic striping between veins. In several cases, unfolding of young leaves, which may be white or yellow. |
Iron deficiency |
: |
Interveinal chlorosis. The entire crop may exhibit bleached appearance. |
5. APPLICATION OF MICRONUTRIENT
i. 12.5 kg of micronutrient mixture formulated by the Department of Agriculture, Tamil Nadu, mixed with sand to make a total quantity of 50 kg/ha is to be applied.
ii. Apply the mixture over the furrows and two thirds in the top of ridges, if ridge planting is followed.
iii. If bed system of sowing is followed, apply the micronutrient mixture over the furrows.
iv. Do not incorporate the micronutrient mixture in the soil.
6. SEED RATE
Select good quality seeds and adopt the seed rate of 20 kg/ha for CO 1 and COH(M) 4 and 25 kg /ha for COBC 1.
7. SPACING
Adopt a spacing of 25 cm between plants in the rows which are 60 cm apart.
Population : For varieties and hybrids 6 – 7 plants / sq. m. and
For baby corn, 8 – 9 plants / sq. m.
8. SEED TREATMENT
Step 1: Use pelleted seeds with insecticides (treat one kg of seeds with Chlorpyriphos 20EC or Monocrotophos 36 WSC or Phosalone 35 EC @ 4 ml + 0.5 gram gum in 20 ml of water) for the control of stem borer or seed treatment with imidacloprid 70 WS 10 g/kg of seeds.
Step 2: Seed treatment with Metalaxyl or Thiram @ 2 g/kg of seed for the control of downy mildew and crazy top
Step 3: Seeds treated with fungicides may be treated with three packets (600 g/ha) of Azospirillum before sowing.

Source: manasaquality.com
9. SOWING
i. Dibble the seeds at a depth of 4 cm along the furrow in which fertilizers are placed and cover with soil.
ii. Put one seed per hole if the germination is assured otherwise put two seeds per hole

Seed sowing operation
(25 cm between plants X rows with 60 cm apart)
10. WEED MANAGEMENT
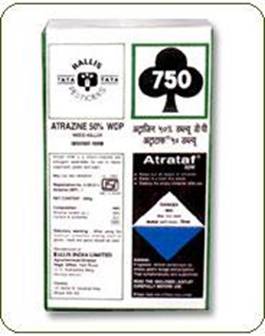
i. Apply the pre-emergence herbicide, Atrazine 50 WP at 500 g/ha (900 lit of water) at 3 days after sowing as spray on the soil surface followed by one hand weeding on 40-45 days after sowing.
ii. Apply herbicide when there is sufficient moisture in the soil.
iii. Do not disturb the soil after herbicide application.
- Hoe and hand weed on the 17th or 18th day of sowing, if herbicide is not applied.
NOTE: If pulse crop is to be raised as intercrop, do not use Atrazine.

Unweeded Maize field


Hoeing and hand weeding on the 17th or 18th day of sowing


Weedfree maize field

11. THINNING AND GAP FILLING
i. If two seeds were sown, leave only one healthy and vigorous seedling per hole and remove the other on the 12-15 days after sowing.
ii. Where seedlings have not germinated, dibble presoaked seeds at the rate of 2 seeds per hole and immediately irrigate.
12. HOEING, HAND-WEEDING AND EARTHING UP
i. Hoe and hand-weed on the 30th day of sowing.
ii. Earth up and form new ridges so that the plants come directly on the top of the ridges. This will provide additional anchorage to the plants.
13. TOP DRESSING WITH N
i. Place half of the dose of N on the 25th day of sowing along the furrows evenly
and cover it with soil.
ii. Place the remaining quarter of N on the 45th day of sowing
14. WATER MANAGEMENT
Maize crop is sensitive to both moisture stress and excessive moisture, hence regulate irrigation according to the requirement. Ensure optimum moisture availability during the most critical phase (45 to 65 days after sowing); otherwise yield will be reduced by a considerable extent.
Regulate irrigation according to the following growth phase of the crop.
Germination & establishment phase 1 to 14 days
Vegetative phase 15 to 39 days
Flowering phase 40 to 65 days
Maturity phase 66 to 95 days

Heavy soils |
Stage |
No. of irrigation |
Days after sowing |
Germination & establishment |
3 |
After sowing, Life irrigation -4th,12th day |
Vegetative |
2 |
25th, 36th day |
Flowering(Irrigate copiously) |
2 |
48th, 60th day |
Maturity phase (Control irrigation) |
2 |
72nd, 85th day |
Light soils |
Germination & establishment |
3 |
After sowing, Life irrigation -4th ,12thday |
Vegetative Phase |
3 |
22nd ,32nd & 40th day |
Flowering phase (Irrigate copiously) |
3 |
50th ,60th & 72nd day |
Maturity phase (Controlled irrigation) |
2 |
85th , 95th day |

Drip irrigation in Maize field

15. HARVESTING
STAGE OF HARVEST
Observe the following symptoms, taking into consideration the average duration of the crop.
i. The sheath covering the cob will turn yellow and dry at maturity.
ii. The seeds become fairly hard and dry. At this stage the crop is ready for harvest.
HARVESTING THE CROP
i. Tear off the cob sheath by using the gunny needle and remove the cobs from the plant.
ii. Carry out harvest operations at a single stage for easy transportation.
THRESHING THE COBS
i. Dry the cobs under the sun till the grains are dry.
ii. Use mechanical threshers or by running the tractor over dried cobs to separate the grains from the shank.
iii. Clean the seeds by winnowing
iv. Collect and store the dry grains in gunnies.

Use mechanical threshers to separate the grains from the shank
STACKING THE STRAW FOR FEEDING CATTLE
- Maize straw can also be used as a good cattle feed when it is green.
- Harvest the crop and cut the green straw into bits with a chaff cutter or chopping knife and feed the cattle.

Dry the cobs under the sun till the grains are dry

RAINFED MAIZE

1. FIELD PREPARATION
Chisel the soil having hard pan formation at shallow depths with chisel plough at 0.5 M interval first in one direction and then in the direction perpendicular to the previous one once in three years. Apply 12.5 t/ha of FYM or compost or composted coir pith besides chiselling, to get an additional yield of about 30% over control.
2. APPLICATION OF FYM OR COMPOST
Spread 12.5 t/ha of FYM or compost or composted coir pith evenly on the unploughed field along with 10 packets of Azospirillum (2000 g/ha) and incorporate in the soil.
3. APPLICATION OF FERTILIZER
-
Apply NPK as per soil test recommendation as far as possible. If soil test recommendation is not available, adopt a blanket recommendation of 60 : 30 : 30 NPK kg/ha for Alfisols and 40 : 20 : 0 NPK kg/ha for Vertisols.
-
Apply half of N and full dose of P2O and K2O with enriched FYM as basal along with Azospirillum (10 packets/ha).
-
Top dress remaining half of N at tasseling.
4. SEED RATE
Select good quality seeds. Adopt the seed rate @ 20 kg/ha for hybrids and 25 kg/ha. for varieties
5. SPACING
Adopt a spacing of 45 cm between rows and 20 cm between plants in the row.
Population : 10 - 11plants/m2
6. PRE-TREATMENT OF SEEDS WITH BIOFERTILIZER
Seeds treated with fungicides may be treated with three packets (600 g/ha) of Azospirillum
7. SOWING
Dibble or drill the seeds at a depth of 4 cm.
8. CROPPING SYSTEMS
-
Intercropping system of maize + cowpea or maize + blackgram is recommended for higher net returns in the red lateritic soils of Southern districts.
-
For Vertisols of Southern district, maize + redgram intercropping systems is ideal.
|























