Irrigation Technology Options for Various Non-Rice Crops
Sorghum- Farmer's practice
Technology options
-
Furrow irrigation once in 15-16 days during first 20 days of sowing and six irrigations with an interval of 6 days during the rest of the crop period
-
Raton sorghum six irrigation viz., at rationing, 4-5 leaf stage, milking, soft dough and hard dough
-
Surge irrigation is feasible in long furrow (>100 m) in level lands
Pearl millet- Farmer's practice
Technology options
Finger millet- Farmer's practice
Technology options
Maize - Farmer's practice
Technology options
Pulses- Farmer's practice
Technology options
-
Blackgram and greengram irrigation at critical stage i.e. one at sowing, second at flowering and third at pod formation with 4 cm depth.
-
Irrigation once in 18 days was optimum
-
Soybean, irrigation at 80 mm, CPE once in 11-12 days interval
Groundnut -Farmer's practice
Technology options
Gingelly - Farmer's practice
Technology options
Sunflower- Farmer's practice
Technology options
Coconut - Farmer's practice
Technology options
-
Irrigation through drip system @ 100 litres of water / tree / day
-
For stress management the palm basins to be opened to a radius of 1.8m with receipt of late showers and mulching can be done
-
Husk mulching can be done to absorb rain water and making available to palm
Application of green manure and FYM in the basin
-
Spreading dried coconut leaves and other organic residues
-
Addition of tank silt to the basin increase the water retaining capacity
-
Under drought situation lower senescent leaves may be removed
-
Pitcher irrigation can be followed where a little water is available
Cotton - Farmer's practice
Technology options
-
Sowing of seeds in ridges and furrows
-
Irrigation at IW / CPE ratio of 0.75
-
Mulching with sugarcane trash @ 5t / ha
-
Spraying of Folicot or paraffin wax 10gm or kaolin 50gm in a litre of water
-
Sprinkler irrigation is feasible
-
Drip irrigation can be adopted
Banana - Farmer's practice
Technology options
-
Irrigation at 0.75-0.9 IW /CPE ratio
-
Chain basin method could be adopted
-
Basins are formed around the suckers and the basins are connected through channels
-
Drip irrigation with high density planting, Fertigations are preferred in favourable locations (well irrigated lands)
-
Gradual widening of furrows with stage of crops. (diagram)
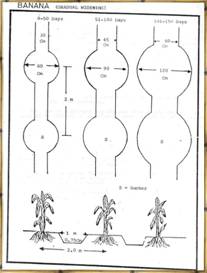
Acid lime -Farmer's practice
Technology options
- Irrigation through drippers at 75 per cent of water supplied through basins
- Drip irrigation is preferred
Tomato- Farmer's practice
Technology options
- Furrow irrigation may be recommended
- Drip irrigation especially with micro sprinklers may also be recommended for hybrids
- Irrigation at IW / CPE ratio of 1.00 during fruit formation And ripening
- Sprinkler irrigation in tomato with 1760m3 gave significantly higher water use efficiency than any other irrigation method
Sugarcane - Farmer's practice
- Excess irrigation through ridges and furrows
Technology options
- Irrigation at IW / PE ratio of 0.9
- Mulching with sugarcane trash in garden land situation reduce evaporation loss
- Foliar application of kaolin @ 12.5 Kg in 750 litres of water per hectare reduce the transpiration loss
- Removal of old dried leaves in 5-7months old crop
- Alternate or skip furrow irrigation can be followed
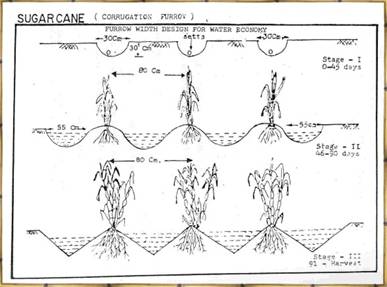
-
Irrigate the field based on sheath moisture percentage
-
In deep trench system of planting 30cm deep trenches are opened at 80cm apart, sets are planted in trenches
-
Drip irrigation with fertigation is highly suitable
-
Surge irrigation may be adopted in long fields in light textured soils
The problems of several non-system tank irrigation system through detailed studies
Encroachment, siltation, soaking of supply channels resulting in poorer / no-inflow of water, pollution of tank water by tannery and dying factory influence (Coimbatore, Erode, Salem Districts)
-
Tank chains almost disappear and their hydrologically interlinking, any improvement could revive the tank will have benefit of exploiting full tank irrigation through appropriate or selective moderanisation benefit
-
Owing to vagaries of man only 50-60 % of supply is realized a crop diversification strategy with non-rice crops is suggested
-
De-silting for reviving the original capacity, tank fore shore, plantation to arrest the silt flow, feasibility of connecting small different tanks into the percolation pond for ground water recharge, rehabilitation of tank structure and inward channels are the solutions eminated from the tank system researches
-
On-farm development structures has to be strengthened the any tank command areas for equitable water distribution from head to tail end along with farmers participation
-
Other technology options for poor quality water
-
Conjuctive use of relatively fresh surface water and poor quality ground water with proper proportions are recommended
-
Growing of salt tolerant crops in the saline water, irrigation belt along with proper drainage facility
-
Community bore wells during the period of erratic water supply in canal command areas enhanced the crop water availability and there by their yields and net returns.
|


