Watershed Development
The ridge to valley approach for executing soil and water conservation measures could be successfully handled only through the watershed concept. If the treatment measures are properly identified according to the location and positive impacts could be generated.
|
|
|
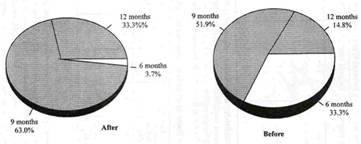
Duration of water availability in the wells influenced by the Percolation ponds in Arasur & Kattampatty DPAP watershed in Coimbatore District |
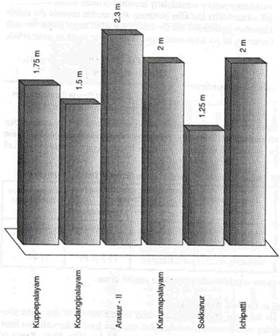
Increase in water table for selected DPAP watesheds
in Coimbatore District |
Possible range of treatment measures
-
Contour bunding
-
Contour trenching
-
Contour stone walls
-
Bench terraces
-
Bunding / Compartmental Bunding
-
Land levelling
-
Summer ploughing
-
Crop demonstration techniques
-
Agro forestry with suitable species
-
Vegetative barriers
-
Basin listing and tied ridging
-
Check dams (Temporary and Permanent)
-
Retaining walls
-
Farm ponds and Percolation ponds
-
Renovation of existing water bodies and inlet channels
-
Fodder plots and live stock improvement
-
Dry land Horticulture improvement
-
Avenue planting
-
Establishing processing and marketing centres
Water table improves water availability in wells increase in irrigated area and soil erosion control are some of the positive results identified in Coimbatore drought prone watershed development programme with participating mode of implementation by the Tamil Nadu Agricultural University.
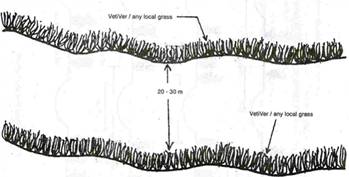
Check dam

Salient features
-
A low weir normally constructed across the gullies
-
Constructed on small streams and long gullies formed by erosive activity of flood water
-
It cuts the velocity and reduces erosive activity
-
The stored water improves soil moisture of the adjoining area and allows percolation to recharge the aquifers
-
Spacing between the check dams water spread of one should be beyond the water spread of the other
-
Height depends on the bank height, varies from a metre to 3 metre and length varies from less than 3m to 10m
-
Cost varies from Rs. 40000/- to Rs. 100000/- per unit
Percolation pond:

Function
To augment the ground water recharge
Salient features
-
Shallow depression created at lower portions in a natural or diverted stream course
-
Preferable under gentle sloping stream where narrow valley exists
-
Located in soils of permeable nature
-
Adaptable where 20-30 ground water wells for irrigation exist with in the zone of influence about 800 – 900 m
-
Minimum capacity may be around 5000 m3 for the sack of economy
-
Also act as silt detention reservoir
-
Cost varies from Rs. 60000 to 150000 per unit
|





