Post Harvest Diseases:: Vegetables:: Chilli
| Bacterial Soft Rot: Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora |
Symptom:
- Dark veinal tissue followed by leaf chlorosis and necrosisInternal dark brown discoloration
- Stem cankers develop - breakage of branches
- Wilting and drying
- Fruit peduncle - highly susceptible & is frequently the initial point of infection
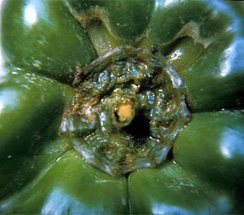
- Both ripe and green fruit may be affected
- Initially, the lesions on the fruit are light to dark-colored, water-soaked, and somewhat sunken
- In later stages, bacterial ooze may develop from affected areas, and secondary organisms follow, often invading the rotted tissue
- Affected fruit hang from the plant like a water-filled bag
|
| |
 |
 |
 |
| |
Soft tissue on peduncle |
Water soaked sunken spots |
Rotten chilli |
|
Identification of pathogen:
- The bacterium is gram negative, rod shaped with 1-6 peritrichous flagella.
|
Management:
Disease incidence could be reduced by
- Early detection of symptoms
- Disinfection of pruning tools
- Avoidance of wounding plants
- Remove plant debris - fallen, diseased leaves
- Seed treatment – 1% sodium hypochlorite for 30 sec, then rinse with clean water
- Avoid planting pepper crops following crops of potato or cabbage
- Rotate instead with crops of bean, corn and soybean
Post-harvest disease management
- Use chlorinated water to reduce populations of soft rot bacteria and to reduce the risk of infection during washing
- Allow fruit to dry thoroughly
- During packing and storage, the fruit should be kept clean and maintained in a cool, dry place
|
Source of Images:
www.avrdc.org/download/publications/crop-guides/peppers/bact_rot.pdf
http://aciar.gov.au/files/mn-157/pdf/TECCIPM-14-%2818Dec13%29-bacterial-diseases.pdf |
|

