-
Macrophomina rot: Macrophomina phaseolina
-
Pink root : Pyrenochaeta tattestris
-
Mosaic
-
Aspergillus rot: Aspergillus niger
1. Macrophomina rot: Macrophomina phaseolina
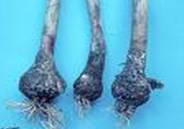 |
Symptoms
- Dough situation in soil favours the occurrence of the disease.
- Rotting of bulb & presence of black sclerotia and pycnidia.
Management
-
Dipping of bulbs in 0.03% formalin or 2% boric acid immediately after harvest helps to avoid or minimize storage rot.
|
2. Pink root: Pyrenochaeta tattestris
Symptoms:
-
The fungus attacks onion from the seedling stage onwards.
-
The roots are affected and they turn pink or reddish and sometimes darken to a red or purple colour black spores form on the diseased roots which eventually shrivel and die.
-
Diseased plants can be easily pulled. The above ground symptoms are shunting and yellowing tip burn and die back of the leaves.
-
Affected seedlings may be killed. Older plants are not normally killed but bulb formation is affected and yields are low.
-
Bulbs are not attacked although the outer scales may be penetrated.
-
New roots are formed throughout the season and these may be infected and killed successively.
Management
3. Mosaic: Garlic mosaic virus
Symptoms
Management
4. Aspergillus rot: Aspergillus niger A. alliaceus , A. repens, A.sclerotionum
Symptoms
-
Rotting of garlic cloves show black, brown, white pink coloured rotting.
-
Rotting may be partial (basal, tip or lesions) or complete.
Management
-
To control this disease garlic bulb should be stored in dry airy place.
-
Infected bulbs should be discarded before storage.
-
Fumigation of bulbs with 0.03% formalin is effective
|

