Post Harvest Diseases:: Vegetables:: Garlic
| Basal rot: Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. garlic |
Symptom:
- Plants - show reduced emergence, yellowing and/or browning (necrosis) of leaves beginning at tips
- Reduced bulb size, bulb decay, and brown, poorly developed root systems
- In storage - bulbs show spongy, sunken, yellow brown rotting lesions
- In early stages - infected bulbs are softened, brown and watery when cut open
- White, light pink or reddish fungal growth covering the cloves or in rot cavities
- Deep cracks form in the cloves, followed by break down of the tissue, which will eventually dry down to a portion of its original size, the cloves becoming crinkled and small
|
 |
 |
 |
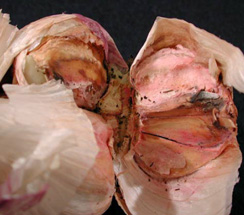 |
| Size reduced bulb |
Small leisons on clove |
Yellow brown rottien lesions |
Deep cracks |
|
| Identification of pathogen:
Mode of spread and survival:
- Soil borne fungus and can persist for long periods in the soil
- Transmission - infested soil on tools or equipment, infected debris, infected seed, or run-off water
- Pathogen enters the plant through wounded tissue
- Disease develops from the base of the bulb and progresses towards the tips of the cloves
- Favored by higher RH and temperatures(20-30°C)
|
Management:
- Avoid rotations with Allium spp.(e.g. onions and leeks) and cereals
- Store bulbs at cool temperatures and low humidity with good ventilation
- Avoid storing damaged bulbs
|
Source of Images:
http://onvegetables.com/2012/07/24/fusarium-basal-plate-rot-of-onion-and-garlic/
http://www.science.oregonstate.edu/bpp/Plant_Clinic/Garlic/Fusarium.pdf
|
|




