Ratoon stunting: Leifsonia xyli subsp. xyli |
Symptoms:
- The affected plants are stunted, the stunting being most severe in stubble and ratoon crops.
- In infected stocks, the presence of pin head like orange coloured dots of bacteria on the internal soft tissue in the nodal region
- The setts taken from diseased plants germinate poorly and the few shoots that are emerged grow very slowly.
Pathogen:
- The organism that causes RSD is, Leifsonia xyli subsp. xyli, a small aerobic bacterium. The genus ofthe pathogen was previously called Clavibacter.
|
 |
|
 |
|
| Stunted growth |
|
Orange pin head dots on internode |
|
|
Management strategies:
Cultural method:
- Select healthy setts for planting.
- Field should maintain at proper sanitation.
- Ungerminated setts should be removed and fill the gap with new setts which should be treated before planting.
Mechanical method:
- Treat the setts with hot water at 50°C for about 2 hours this gives 100 per cent control. A temperature higher than this would kill the cane and lower temperature than the specified enables the pathogen to survive.
- Aerated steam therapy eliminates the pathogen from the infected canes. Use of disinfectants to clean seed cutting tools which would reduce the chance of spread of pathogen from the infected to healthy setts.
|
| |
 |
|
 |
| |
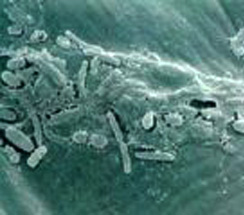
Leifsonia xyli |
|
Microscopiv view |
|
Chemical method:
- Chemical disinfectants that may be used on cane cutting knives includes, Lysol, Dettol, ethanol, Mirrol and Roccal. Atleast 5 minutes of contact with the cutting surface is needed to assure disinfection.
|




