Sett rot:Ceratocytis paradoxa |
Symptoms:
- When diseased setts are planted they may rot before germination, or the shoots may die after reaching a height of about 6-12 inches.
- As the setts get dried up, the reddish colour becomes black with lots of black coloured fungal spores adhering to it.
- If infected shoots survive, they are very much stunted and chlorotic.
- Eventually the leaves may wither and the shoots wilt.
- If the affected shoots and setts are examined the central portion of the shoots will be seen discoloured red and the contents of the sett rotting.
- When split opened, the affected setts exhibit pineapple odour.
|
| |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| |
Reddish discolouration in cane |
Stunted growth |
Yellowing and sunted growth |
Black fungal spores |
|
|
Pathogen:
- Ceratocytis paradoxa is initially whitish, measuring about 5 mm in diameter and colonies turn black due to the production of chlamydospores, which are heavily pigmented, when mature.
Management strategies:
Cultural method:
- Healthy setts should be obtained from disease free fields
- Proper drainage and planting of setts in 1-2 cm depth.
- Field sanitation practices combined with chemical pre treatment of the setts are quite effective in controlling the disease
- Avoid deep planting during monsoon season
Chemical Method: |
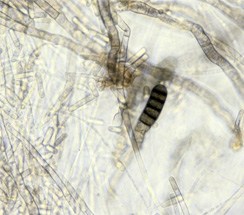 |
| Ceratocytis paradoxa |
|
- Dipping the setts in 40 ppm of boron or manganese, or spraying the plants with either of these minor elements reduces the disease intensity.
- sett treatment with fungicide like Bavistin, 0.1 per cent before planting
- Apply carbendazim @ 2gm/lit of water at the root zone area and same as follow at 15 days interval
|





