Agricultural crops :: Cash crops :: Tobacco
Black shank: Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae
Symptom
-
Black shank occurs sporadically in every type of tobacco and causes more damage, to tobacco grown under high rainfall or irrigated conditions in light soils of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat.
-
It is caused by soils inhabiting fungus Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae and appears both in nursery as well as in the field.
-
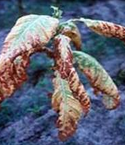
In nursery the affected seedlings show blackening of roots and stem near soil. Under wet weather conditions the conidial infection spreads to leaves, which show water soaked lesions resulting in leaf blight and collapse.
-
The leaf blight phase of the disease, though rare in occurrence spreads very rapidly during cloudy and continuous cyclonic weather resulting in heavy damage.
-
Under such conditions large circular, black or brown water-soaked lesions appear on the basal leaves.
-
In the field blackening starts at the collar region and spreads both downwards and upwards causing rotting and necrosis of the whole stem including basal leaves.
-
First sign of infection seen in the vigorously growing plants is yellowing of leaves, sudden wilting and ultimately death of plants under warm weather.
-
The disease appears in scattered patches in the field. The stems of such plants when split open show brown to black dried pith in disc like plates characteristic of black shank.
|
|
Management
-
It can be checked in the nursery by rabbing the seedbeds or drenching the seedbeds with 0.4% Bordeaux mixture 2 days before sowing to minimize the initial inoculum potential.
-
Subsequent application of fungicides like 0.2% Copper oxychloride is essential for checking leaf blight and seedling blight.
-
At the time of transplanting, seedlings with blackened stem should be discarded to prevent spread of disease to field.
-
Sanitary measures like removal and destruction of the affected plants and disinfecting the spots with 0.4% Bordeaux mixture drench will prevent spread of the disease in the main field.
-
Leaf blight phase of the disease can be checked by spraying 0.2% Mancozeb.
|
|