| Rhizopus rot: R. stolanifer |
Symptom:
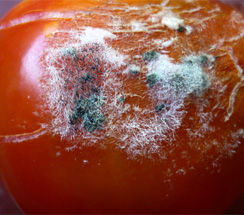
- On tomatoes, Rhizopus rot appears water-soaked and may exude a clear liquid
- Lesion surface may be covered with thin, cotton-like fungal structures (especially under humid conditions).
- Dark sporulation may crown the white tuft of Rhizopus.
- mycelium can infect adjacent fruit through natural openings or mechanical wounds, creating nests of mold and diseased fruit
|
| |
 |
 |
 |
| |
Cotton-like fungal structures |
Dark sporulation |
Infected tomato |
|
Identification of pathogen:
Penetration:
- Wound - cause ripe fruit to rot-Fermentative odour
- Fruit surf. – extramatrical whiskery mycelium, black sporangia
- Range of temp. 5, 15 and 25°C reaching disease incidence of 97-100% RH
Spread:
- Air currents pathogen grows very aggressively even on refrigerated fruit.
- Pallets and cartons, and it may survive for months in fruit residues left in picking containers and field bins.
- The length of the surface wetness period needs to be longer at the lower temperatures for disease development
|
Management:
- Ensure good drainage facility
- In the greenhouse, maintain a RH of less than 80%, during the night
- Remove decaying plant material from the plant bed
- Avoid bruising during packing and transport
|
Content validator:
Dr. M. Deivamani, Assistant Professor, Horticulture Research Station, Yercaud-636602.
Source of Images: http://farm5.static.flickr.com/4039/4371503927_e71aa7deea.jpg
http://www.apsnet.org/publications/imageresources/PublishingImages/2014/fi00219.jpg
|



