| Early Blight: Alternaria solani |
Symptom:
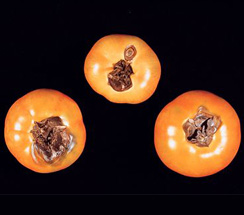
- The fruit become infected-through the calyx or stem attachment, either in the green or ripe stage. Concentric ring present on the fruit surface.
- Appear leathery and may be covered by a velvety mass of black spores.
- Infected fruit frequently drop, and losses of 50% of the immature fruit may occur.
|
| |
 |
 |
 |
| |
Early blight |
Black spores |
Infected tomato |
|
Identification of pathogen:
Fungus:
- Mycelium- septate, branched, light brown, become darker with age
- Conidiophores- 50 to 90μm in length and dark coloured
- Conidia-beaked, muriform, dark coloured and borne singly
Favourable condition:
- Maximum dispersal of conidia- 9am and 12 noon
- plants suffering from water stress- susceptible
Spread and survival:
- Spread by wind and rain splashes
- Under dry conditions- survives in infected plant debris in the soil for 3 yrs
- Seed borne
|
Management:
- Use disease free seeds for sowing
- Field sanitation
- Crop rotation with non solanaceous crop
- Optimum irrigation- to avoid stress condition
- Seed treatment- thiram 2g/kg
- 3 sprays with difolatan 0.2 % at fortnightly interval
|
Content validator:
Dr. M. Deivamani, Assistant Professor, Horticulture Research Station, Yercaud-636602.
Source of Images:
http://wiki.bugwood.org/Alternaria_solani_%28Early_blight_of_tomato%29
http://www.apsnet.org/edcenter/intropp/lessons/fungi/ascomycetes/Pages/PotatoTomato.aspx
|



