| Phoma Rot: Phoma destructiva |
Symptom:
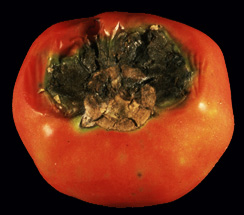
- Distinguished from other rots by the black color of this spot
- Small, black, pimple-like eruptions.
- Specks are the pycnidia or fruiting bodies of the fungus.
- Moderate temperature and high humidity.
|
 |
 |
 |
| Pimple like black eruption |
Fungal spores |
Cross section of infected tomato |
|
Identification of pathogen:
Fungus:
- Mycelium- septate, branching & hyaline, becoming dark with age
- Pycnidia – subcutaneous and later erumpent, dark subglobose
- Pycnospores- hyaline, subglobous
Favourable condition:
- moderate temperature and high humidity.
- Most rapid decay on ripe fruits @ 21°C, but since tomatoes ripen more rapidly at about 23°C, the disease may be more promptly in the ripening room
Spread and survival:
- Seed borne
- By infected transplants or rain-splashed from infected crop debris
- Fruits – wounds, stem scars
- Progress is more in ripe than in green fruits
|
Management:
- Seed treatment – ceresan dust (5% ethyl mercury phosphate)
- Seed be sanitation
- Do not harvest when plants are wet
- To control contamination in packing process- 5% borax solution containing 0.5 % liquid tar soap as washing medium
|
Content validator:
Dr. M. Deivamani, Assistant Professor, Horticulture Research Station, Yercaud-636602.
Source of Images:
http://erec.ifas.ufl.edu/tomato-scouting-guide/diseases/phoma-rot.shtml
http://gardener.wikia.com/wiki/Phoma_rot
|



