|
Abortion
| Nature of disease |
|
- Expulsion of a dead or live recognizable size fetus at any stage of gestation (45-60 days onwards to parturition) is called as abortion.
- This may be due to various causes.
|
| Casuses |
|
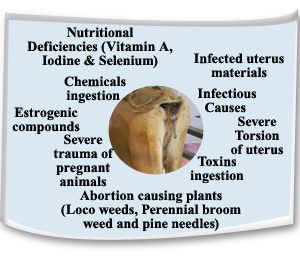
- Infectious conditions such as Bovine Viral Diarrhea (BVD), Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBRT), Leptospirosis, Brucellosis, Mycotic abortion, Actinomyces, Trichomoniasis, Campylobacteriosis, Listeriosis, Chlamydiosis, and Epizootic Bovine Abortion may cause abortion in cattle.
- Severe trauma, severe torsion of the uterus and twinning may cause abortion.
- Toxins can cause abortion in cows.
- Coumarins from rat poison and moldy sweet clover can cause abortion.
- Nitrates, chlorinated napthalenes, arsenics can cause abortion.
- Locoweeds, perennial broom weed and pine needles can cause abortion.
- Estrogenic compounds may cause abortion.
- Douching and infusion or Artificial insemination of the pregnant animals causes abortion.
- Vitamin A, iodine and selenium deficiencies can cause abortion.
|
 |
| |
 |
| Clinical symptoms |
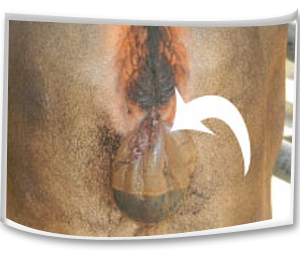
- Protrusion of fetal membranes or water bags from the vulva prior to expected date of calving.
- Discharges from the vulva.
- Spontaneous expulsion of a dead or live recognizable size fetus without full development.
- Anorexia, dull and depressed condition of animal.
|

 |
| |
|
 |
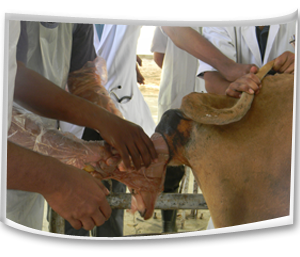
| Prevention and Control measures |
|
- Proper disposal of the aborted fetus and its membranes.
- Prevention of infected materials (uterine discharges, fetal membranes) ingestion.
- Always the animal shed should be clean.
- To prevent abortion due to Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis and Infectious Pustular Vulvovaginitis (IBR-IPV) pregnant cows at any stage of gestation should not be vaccinated with IBR-IPV vaccine. Vaccination can be carried out in heifers at 6-8 months of age.
- To prevent abortion due to listeriosis, feeding of poor quality silage with high pH should be prevented.
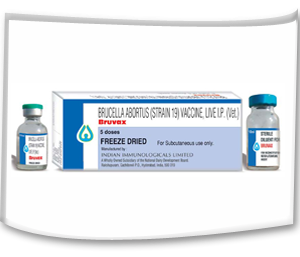
- To prevent abortion due to brucellosis, vaccination of calves from 3 to 7 months of age with strain 19 Brucella vaccine and bull calves should not be vaccinated.
- Breeding should be stopped at disease outbreak.
- Contact between animals should be kept at a minimum during outbreak.
- Diseased bulls should not be used for breeding.
- The semen which is used for Artificial Insemination should be free from any infectious agents.
- Pregnant animals should be protected from other animals attack.
- Pregnant animal sheds should not be slippery.
|
 |
| |
 |
|