Botany And Climate
About Sugarcane
Vernacular Names
English: Cultivated Sugarcane, Noble Cane, Noble Sugarcane, Sugar Cane. Hindi: Ganna, Sakhara, Ukh. Tamil: karumbu Malayalam: Karimbu, Karimpu Kannadam: kabbu |
 |
Origin
Sugarcane originated in New Guinea where it has been known since about 6000 BC.The cultivated canes belong to two main groups: (a) thin, hardy north Indian types S.barberi and the Chinese S.sinenses and (b) thick, juicy noble canes S.officinarum. Highly prized cane is S.officinarum. The origin of S.officinarum is the Indo-Myanmar China border with New Guinea as the main centre of diversity. The officinarums are called the "noble canes' due to thick, juicy, low-fibred canes of high sucrose content. The origin of S.robustum is New Guinea. The origin of S.spontaneum is subtropical India. The habitat of these two wild canes is swamps, river banks, water courses etc. Tropical cane (Thick cane) might have originated in New Guinea. From India it spreads probably to China, Arabia, Egypt and Sicily.
Introduction
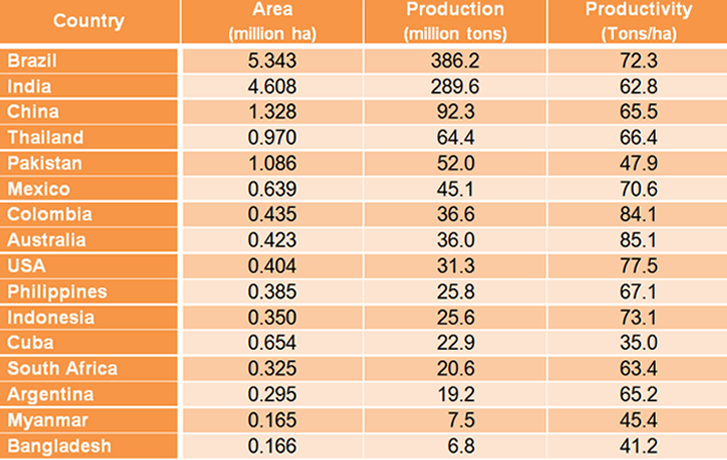
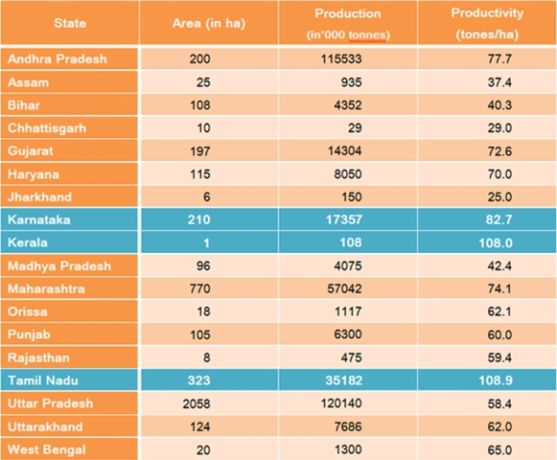
Sugarcane and sugarbeet are the main sources of sugar in the world. Out of total sugar produced in the world 60 per cent is obtained only from sugarcane. Asia is the largest producer of sugar followed by Europe Most of the sugar in Asia comes from sugarcane whereas in Europe from sugarbeet. Presently sugarcane is grown in an area of 16 m. ha in over 79 countries. The global production of raw sugar is 112 m.t. India stands first in area (3.93 m. ha) and production (167 m.t) among the sugarcane growing countries of the world. Uttar Pradesh has the largest area almost 50 per cent of the cane area in the country, followed by Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Bihar, Haryana and Punjab. These nine are most important sugarcane producing states. Sugarcane production is also highest in U.P. followed by Maharashtra. Productivity wise, Tamilnadu stands first with over 100 tonnes per hectare followed by Karnataka, Maharashtra. Bihar has the lowest productivity amount the major sugarcane growing states. The sugar industry is the second largest agro-based industry, next only to textiles, in the country.
Classification of Sugarcane
Family - Gramineae
Class - Monocotyledons
Order - Glumaceae
Sub family - Panicoidae
Tribe - Andripogoneae
Sub-tribe - Saccharininea
Botanical Description
Sugarcane is a tall perennial tropical grass, which tillers at the base to produce unbranched stems from 2-8 m more tall, and to around 5cm in diameter; it could be called as giant grass. It is cultivated for these thick stems or stalks or canes, from which the sugar is extracted. The botany of cane consists of root, leaves, stem and inflorescences.
-
Root
-
Stem
-
Leaf
-
Inflorescence
Root
|
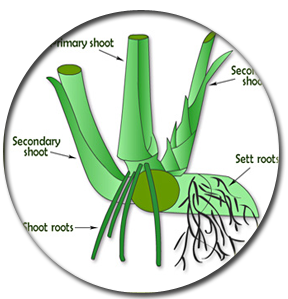 |
Stem
|
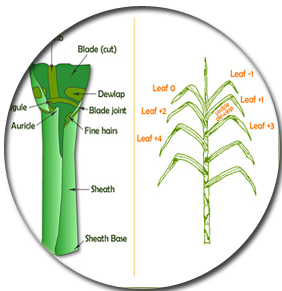 |
Leaf
|
 |
Inflorescence
|
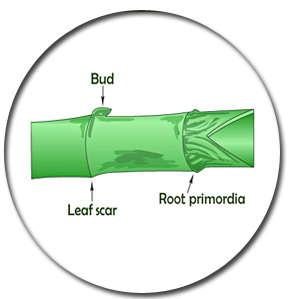 |
Climate
Sugarcane is a tropical plant. It grows more successfully in those regions where the climate is more or less tropical but it can grow in sub tropics too as in north India. Sugarcane is grown in the world from altitude 35° N and 35° S, from sea level to 1000m of altitude or little more.
Climatic factor
Latitude and altitude:
Sugarcane is grown in the world from altitude 36.7° N and 31.0° S, from sea level to 1000m of altitude or little more.
Rainfall:
A total rainfall between 1100 and 1500 mm is adequate provided the distribution is right, abundant in the months of vegetative growth followed by a dry period for ripening. It also grown in area where rainfall is low upto 500 mm. Above 1500 mm rainfall cause lodging of cane.
Temperature:
Growth is closely related to temperature. It has a wide temperature range from over 38°c. Optimum temperature for cane growth (germination) is 27° to 33°c (80 to 90°F). Temperature below 27°c definitely injurious to the cane, reduce tillers and above 38°c adversely affect the sprouting.
Ideal temperature:
Carbon assimilation-30°c
Sugar synthesis-30°c
Sugar transport- 30-35°c
Tillering-33.3-34.4°c
Root growth- 36°c
Shoot growth- 33°c
Relative humidity:
High humidity (80-85%) favours rapid cane elongation during grand growth period. A moderate value of 45-65% coupled with limited water supply is favourable during the ripening phase. Above 40% humidity coupled with warm weather favours vegetative growth of cane.
Sunshine:
|
Frost:
|
Wind:
High velocity winds exceeding 60 km/hr are harmful to grown up canes leading to lodging and cane breakage. StatisticsArea,Production and Productivity of sugarcane in World
State Wise Area,production and productivity of Sugarcane in India (2008-2009)
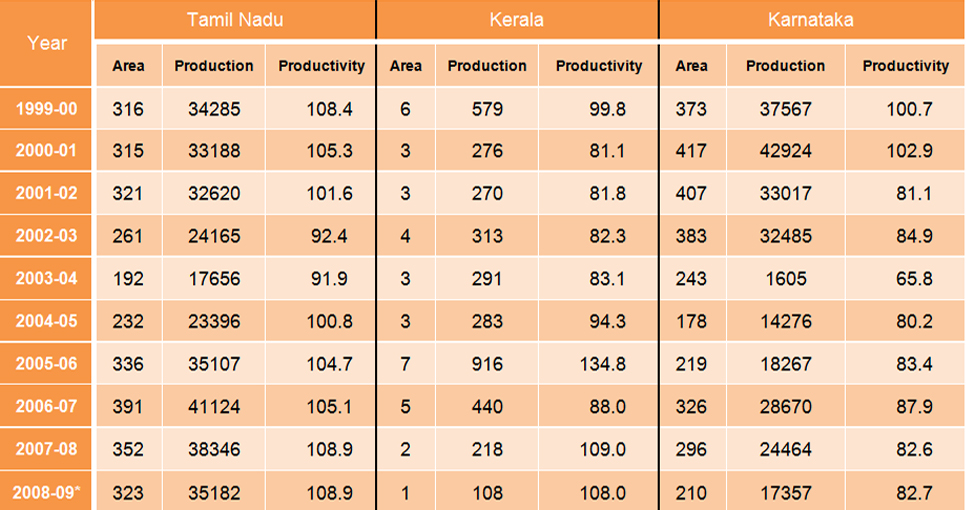
Sugarcane Statistics for Tamil Nadu,Kerela and Karnataka (1999-2009)
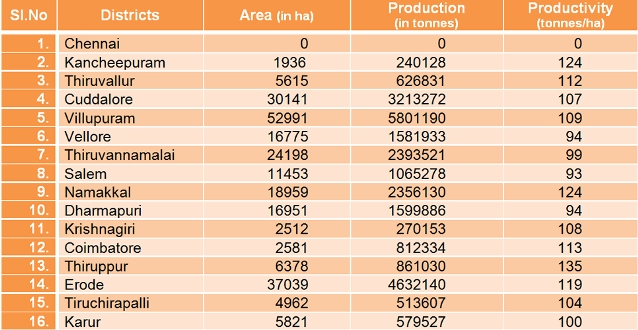
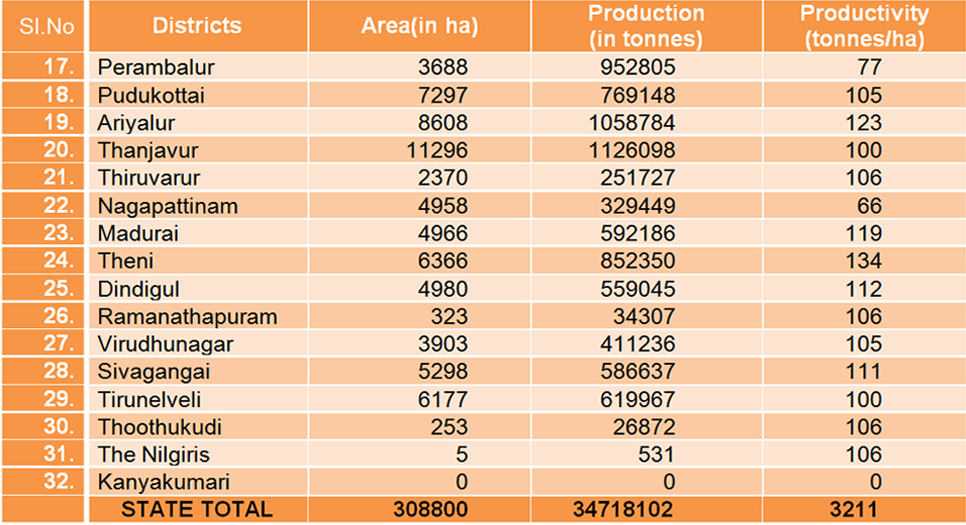
District wise Area,Production and Productivity of sugarcane Area, Production and Productivity of Sugar cane (2007-08)
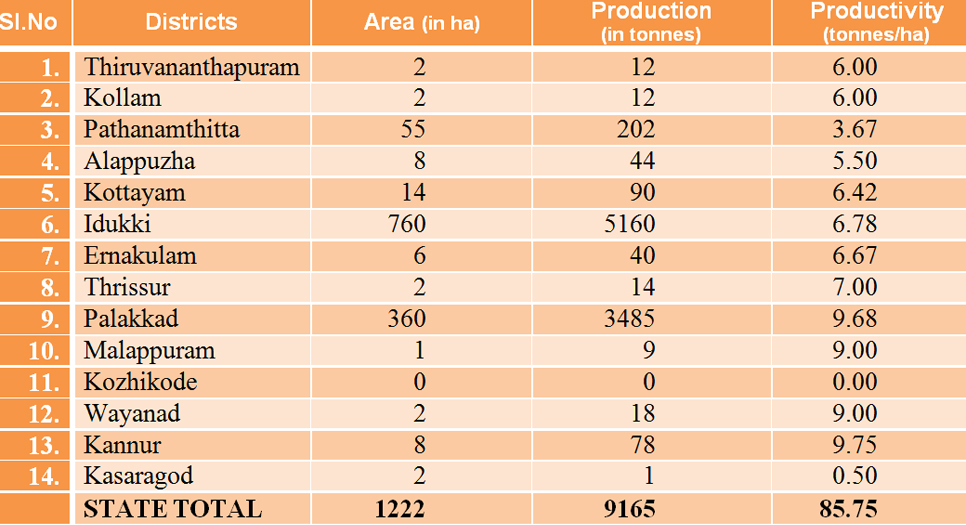
KERALA Area, Production and Productivity of Sugar cane (2006-07)
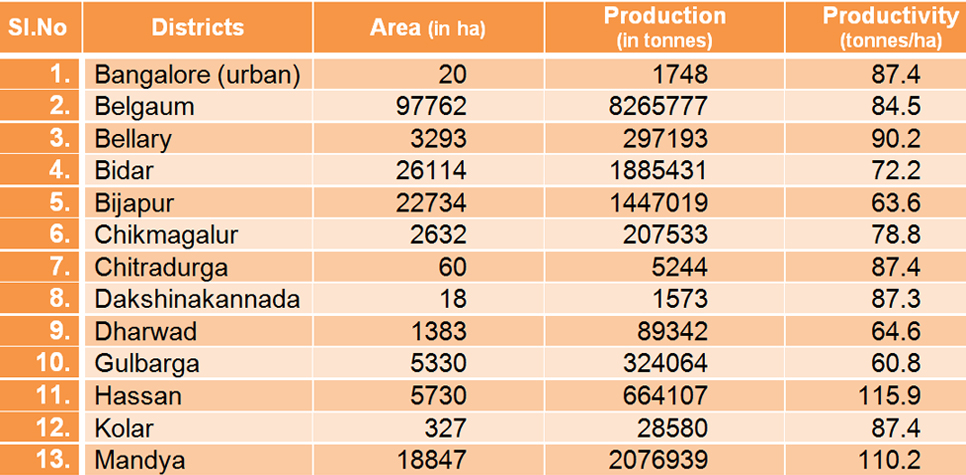
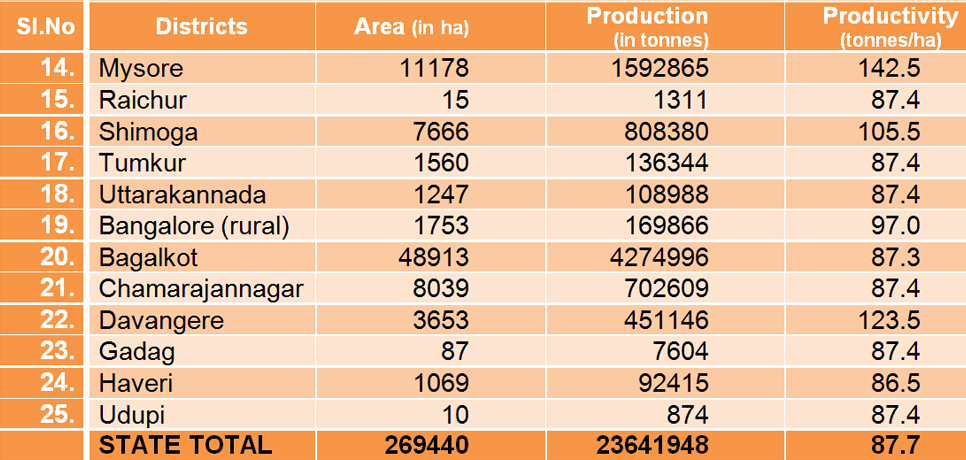
KARNATAKA Area, Production and Productivity of Sugar cane (2006-07)
|