Compost Preparation
The substrate for cultivation is specially prepared compost. The mushroom houses should have the facilities for temperature control and pasteurization. Buildings are constructed of wood or hollow cement bricks or double walls. The shed is partitioned into small compartments and provided with trays. Environmental conditions like temperature, relative humidity and ventilation are controlled inside the shed by installing suitable equipment.
Compost is the substrate in which the mushroom mycelium grows and on which it produces fruiting bodies. It is the product of a fermentation process brought out by a number of mesophilic and thermophilic microorganisms that decompose plant residues and other organic and inorganic matters. The quality of compost influences the yield of mushroom. Compost prepared out of horse manure and wheat straw is ideal one. Since these materials are not easily available, many substitutes are suggested and are in use. There are two methods of composting, Long method and short method. The distinction is based on the time taken for composting and the long method needs three to four weeks, while the short method requires only 12-15 days, since the composting process is hastened by pasteurization. In the long method of composting, pasteurization is avoided, which will make the compost poor in quality and often gives variable yields.
Long Method
The composting is done on a cement floor. It can be done in the open or under a roof, but sides are to keep open.
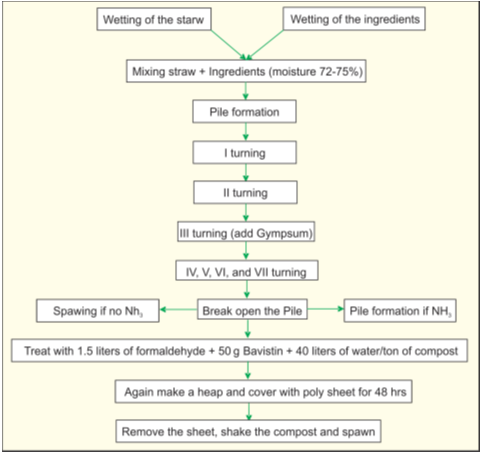
Flow chart of Long Method Composting
a)Natural compost:
This compost is traditionally prepared by using horse manure and the barn waste consisting of straw bedding of wheat of barley. These are taken in the proportion of 4:3 and to this mixture, generally 100 kg of chicken manure and 5 kg of urea are added per tonne of substrate. The manure is kept as heap of about one metre height and is regularly examined and turns down repeatedly when it emits ammonia smell. This is o be done for every three – four days. Finally every tone 25-kg of gypsum is added.
b)Artificial Compost:
Many formulae are available and ingredients to be used vary according to the locality and availability of materials. A widely used formula in india is is given below:
| Formula |
Quantity |
| Wheat straw (chopped to 8-2- cm) |
250 g |
| Wheat bran |
25 kg |
| Ammonium sulphate of Calcium ammonium nitrate |
4 kg |
| Urea |
3 kg |
| Gypsum |
20 kg |
Chopped wheat straw is spread over the floor and water is sprinkled thoroughly to wet the straw. Mix all the ingredients except gypsum. Finally the mixture stacked to a height of one metre and compacted using wooden boards. This mixture is turned periodically on 5th , 10th, 14th , 18th, 22nd and 26th day. The gypsum is added in two equal splits on the 14th day and 18th day. It is advisable to add nematicides like nemagon on the 22nd day @ 40-50 ml per tone of substrate. In mushroom houses where insect pests are also a problem, 10-15 ml of malathion is also added during the final turning and sufficient quantity of water is also added on the heap.
Short method
The short-term compost involves two phases of operation, Outdoors composting and steam pasteurization. The commonly used formula is give below
| Formula |
Quantity |
| Chopped Wheat Straw |
100 g |
| Chicken manure |
400 kg |
| Barley |
72 kg |
| Urea |
14.5 kg |
| Gypsum |
30 kg |
Compost Production by Short Method
Phase: I Outdoor Composting:
Barley and chicken manure are added to wheat straw and stacked after adding sufficient water to completely wet the same. The stack can be 3.3 X 2.5 X 1 m size. Turnings are given on the 2,4,6 and 8th days. The pH to be adjusted to 8.5 and the compost filled into trays for pasteurization.
Phase: II Stream Pasteurization
Stream or dry heat is introduced to establish an aerobic fermentation and the temperature maintained between 52 -60° C inside the compost. Usually it is done in a room well insulated where the trays are properly kept and after this all ventilators are closed and steam is introduced to raise the temperature to 52-54° C for four hr and afterwards fresh air is introduced and steam supply cut off.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN LONG METHOD OF COMPOSTAND SHORT METHOD OF COMPOSTS FOR BUTTON MUSHROOM
| Properties |
Short Method |
Long Method |
| Days required for compost Preparation |
16 to 20 |
28 to 30 |
| Selectivity |
Complete |
Partial |
| Average yield (Kilo/ 100 kilo compost) |
18 to 25 % |
10 – 15 % |
| Effect on environment |
Less polluting |
Polluting |
Average compost production / ton of
Straw |
2.0-2.5 tons |
1.75-2.0 tons |
| Average final N % in Compost |
2.0-2.2 |
1.75-2.0 |
| Prewetting area for 20 tons output compost |
60 x 40 ft |
- |
| Infrastructure required for 20 tons output compost |
Covered composting yard (60 x 40 ft) + 1 tunnel (36 x 9 x 12 ft) |
Outdoor composting yard (60 x 40 ft.) |
| Man days required for 20 tons compost output |
20-25 |
30-35 |
| Power requirement for 20 tons output compost |
700-900 KW |
Nil |
| Compost handling equipments required (Large farm) (> 500TPA) |
Turner, filling line, hopper regulator, Bobcats |
Nil |
| Environmental Impact |
Causing Less Impurities |
Causing excess Impurities |
| Percentage of Nitrogen in compost |
2.0 to 2.2 % |
1.75 to 2 |
| Labors for producing 20 tons compost |
20 to 25 |
30 to 35 |
| Construction cost for 20 tons compost |
Floor for producing compost (60 x 40 feet)36 x 9 x 12 feet scale covering room |
Floor for producing compost (60 x 40 feet) |
| Usage of Current for producing 20 tons compost |
700 – 900 KW |
- |
Updated on Dec 2013
|