Pepper production in Organic farming
Pepper cultivation play a key role in India's exports. It is cultivated in Kerala, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. In Nature, agricultural practices pepper can be cultivated as main crop as well as inter crop.With inputs from the harvested crop to be grown up to 25 m apart.In Sloping areas take necessary precautions to prevent drainage of chemical cultivation land water in to nature agriculture land.
Varieties :
Panniyur 1,2,3,4,5 Kirimunta, Kottanatan, Supakara, Panchami, Pournami, Ottappilakkal 1, Kalluvalli, Palankotta, IISR Sakthi, IISR Dhevam, IISR kirimunta, IISR Malabar Excel and Utiran Kota. |
 |
Panniyur 1 variety is a hybrid variety. It spread well in the trees. It gives extra yield, rather than the other varieties. Panniyur 5shadow tolerant variety. It is generally suitable to grow in arecanut gardens. |
Panchami :
2828 kg of dried
pepper / ha
Cirikara:
2677 kg of dried pepper / ha
Malabar Excel :
2.78 kg of dried pepper / vine
Devam:
6.14 kg of dried pepper / vine
Kirimunta:
6.14 kg Green pepper / vine
PLT -2
4.97 kg green / vine
Subhakara:
4.2 kg Green pepper / vine
Pournamy:
4.7 kg Green pepper / vine
Soil and climate :
Pepper crop mountainous areas like Kanyakumari, Nilgiris, Keelbhavaniin Tamil Nadu, are mostly cultivated. Grows well in well in drained soil. In clay, sandy lands, the crop does not grow well. If the soil pH is between 4.5 to 6.6 is better. Pepper crop needed rain and high temperatures. Up to a height of 1500 meters above sea levelmountains, where the crop grows well in the.
Season :
June – December the high quality pepper crop is cultivated in rainfed.
Breeding :
Pepper crop breeding was done by vein cutting method. One meter long pepper vein can be taken with 2 or 3 nodes from the mother vein can be sown in polythene bags. After the transplantation, the use of rooted cuttings. After the cutting gets root, the transplantation will be done.
Seed and planting :
Nursery production :
In a area where a good source of shade with water drainage facility, prepare1 meter wide and 5.6 meters long beds. After dig the soil prepare the beds. In each bed apply FYM 12 kg, 5 kg of vermin-compost, 250 gBio fertilizer mixed with 5 kg sand and 5 kg red soil.
To choose the runner shoots grow on the base of the parent vine with desirable qualities. Near the selected runner shoots, stick the support in the soil and bind the vine in to the support. Do not allow the runner shoots to get root in the soil. In the month of February, March with a 2-meter length of the runner shoots is to be cut from the mother vine and remove. At the top of the one third of the runner shoots and bottom of the one third should be removed and middle part will choose to prepare cutting. Young runner shoots and old runner shoots should be avoided. Cut the shoot with 2-3 nodes to produce with a knife. These stem piece’s bottom should be dipped 30 minutes with Panchagavya 3% solution and then planting it in to the bed or polythene bags.In polythene bags (7x5-inch size), to fill with a part of the fertile top soil, one part river sand, one part Vermi Compost is a mixture of cow dung. |
| Panchami |
Cirikara |
 |
 |
| Devam |
Malabar Excel |
 |
 |
| Kirimunta |
Subhakara |
 |
 |
| Subhakara |
Pournamy |
 |
 |
|
|
One acre in the nursery beds supplying 250 gramsazhosPirillum, 250 grams of phosphobacteria root internal fungaland then mix with soil.Small holes need to be applied before the application of the fertilizer mixture in bags. Beds or polythene bags after planting stem cuttings pour enough water and put in a shade. Pour the desired amount of water to the lawn sprinkler.At the time of Developing small-budded, take 300 ml of panchagavyamix with10 liters of water and pour once in 15 days.Canopy or bamboo, polythene bags lined with polythene which sets shelters are arranged. The third week the stem cuttings rooted in polythene bags and ready for planting.
Planting pepper and shrubs :
Spined drumstick, zucchini, Silver Oak and Shubabul actively promoted for climbing base tress of pepper crop. When intercropping cultivation of jack, kamuku and coconut.Spineddrumstick, Zuchini are cut stems used for planting. Plant this stems one or two months before planting of pepper vines. Three or four years before planting seedlings Pepper vines, the climber tree seeddlings to be planted.
Bio-fertilizers and bio-regulators :
Well decomposed farmyard manure 12.5 t/ha, 5 tons of natural bioenergy fertilizer, 5 ton of Vermi Compost and 1.25 ton well-composted coconut fiber manure should be applied. Alongside supplying bio-manure, azhospirillum,phospobacteria, azitofactor and root internal fungal to be applied at the rate of 25 kg each and Apply Trichodermaviride and Pseudomonas florescenceat 2.5 kg each/ha. Along this apply 25kg of rock phaphate.Before planting of stem cuttings in the pits aforementioned bio-fertilizer, bio-organic fertilizer mixture and mix well to pit against the antibiotics to be applied at the rate of 40 kg.
Land preparation :
Sloping soil and water conservation measures in the areas of sufficient size to take when preparing to land.
Planting :
Recommended variety to be useed.Using of Erythrina variety reduce the Nemotodes. In one pit 2 to 3 rooted stems can be planting during the rainy season in the months of June and July.
To plant the support trees, 15 cm distance 50 cm distance 50 cm length and width dig the pits. At the time of planting in the pits, apply each 10g Azospirillum,Phosphobacteria and root internal fungal. Along with 25g Magnesium sulphate and 30g rock phosphate for each pit. For one hectare we can plant 1600 stem cuttings with the spacing of 2.5x2.5 meters.
Crop management :
As the vines grow, to avoid the veins to touch the soil. So tied the vines in supporting trees. Young veins affected the drought in summer time will be set around the shade.When the rooted vines grow allow the sunlight and maintenance should be undertaken in order to grow straight.
At the stage of flowering, to control the insect and fungal attack, avoid excessive shade.In these cases, the highest branches of the supporting trees to be cut and mulching pruned branches or use as bio manure.
Mulching :
Mulching can be done with Green and dry leaves. You cannot do much damage to the base of the vine. Take the weed has to do mulching. Using cover crops such as Kalappakoniyam, Mukoniyatis, Mimosainsisa during the rainly season for control of soil erosion and weeds. Plant the legume crops in walkable area sides and field edges to control the soil erosion.
Fertigation :
A year after the vines are well-developed, 5 kgwell-decomposed farmyard manure, 5 kg bio manure and 5 kg of vermicompost during May - June and October - November month may be applied in the soil. On the basis of soil analysis, rock phosphate, bone-meal, such as limestone and dolomite can be apply. Apply sawdustin soils which has low Potassium content.Green crop residue, cow dung, poultry waste and sawdust (or) mixed with rock phosphate used in place of chemical fertilizers. Apply 2 kg need seed powder for year for one vine, where the vine affected by the nematodes.
Application of lime :
For two years, 500 grams of lime or dolomite to be applied.
Water management :
Capability for the irrigation can supplied water around the pit for December – May month once in 10 days.Drip irrigation is suitable.
Weed Management :
Weeds can be removed during June – July and October – November months (a month two times).
Pruning :
Pepper vine tips can be pinched to improve the lateral branch growth.In the first two years of pepper vine remove the nut to pull out all the bouquet. To increase the growth off shoots leaves pick out the selected leaves.Pepper creep touching the height of the supporting trees, after that the lack of support the vines creep hanging downwards. Remove it and the stems can be used to produce seedlings. |
Insects :
Clubs beetle: It is yellowish-purple colour small beetle. This beetle eat the tender pepper skin. Beetle’s larvae put the hole and damage the tender pepper.
Mealy bug and scale insects : The leaf, vine and fruit juice to absorb and damage from strings.
Leaf roller : It was within the young leaf curl and sucking the juice.So rolled part will be damaged. The morphological structure of green leaf green leaf loss its colour.
Control Measures :
To control clubs beetle, mealy bug, scale insects and leaf roller spray neem oil (400 ml with 100 litres water) at the time of flowering during July and October. And also spray Dasakavya 3% solution 3 times with 15 days interval. To control the insects may spray garlic, Asafetida sap 3% solution.
Nematodes :
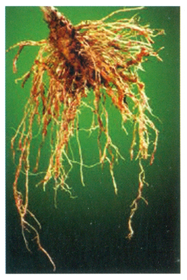
Nematode affected vines, impacted by the reduced height of vines, small leaves and colour change in to pale yellow and nodes can found in the roots.
Control measures :
- At the time of selecting the vines, we can choose nematode free plant.
- If nematode problems is highly identified, marigold can be planted to control nematodes.
- Pecilomicis and Trichoderma fungus and Pseudomonas bacteria mixer can be applied in the root zone at the rate of 50 grams per vine.
- Neem cake mixed with farmyard manure at the rate of 100 grams may be applied.
|
| scale insects |
Clubs beetle |
 |
 |
| Root knot Nematodes |
scale insects |
 |
 |
|
|
Diseases
:
- Foot rot disease : Foot rot disease caused by fungi paittoptorakepsisi. To control the disease, should undergo regular health operations. With limited time to undertake plowing. Water should flow in a balanced manner. Trichoderma, Pseudomonas mixture should be applied at the rate of 50 grams per year for each vine.
- Clubs disease :clubs disease caused by a fungus that KolattodrycomKiliyosboriyatis. Clubs disease (or) resistance appears to rot appears, spray Bordeaux mixture 1% to the lowest level. Stunted growth and disease factor seeds should not be used for cultivation. Neem seed powder can be used to control the disease.
|
 |
 |
 |
| Foot rot disease-1 |
Foot rot disease-2 |
Clubs disease |
|
- Slowly rot and rot disease outbreaks: Rot disease is a main disease,which affects the pepper vine. Well grown pepper vine suddenly damping off.It is a type of fungal disease.It's July - August, the southwest monsoon rains caused rampant. If the disease affects the vine within 10 - 15 days the entire leaves drop and the plant will die. Falling leaves is in green colour. For the most part, raised in nearby spruce and mature leaves become dark. Spruce part first decomposing and then root scorched and the plant decays. This disease mostly seen in lower Palani hills.
Harvest and Post Harvest Vulnerabilities :
After planting the pepper vines, starting in the third year it give yield, in the sixth year these vines give good yield. 6 to 7 months after the onset of flowering in pepper ready for harvest.In India, pepper vine flowers that bloom in May-June.From bloom to harvest is 6-8 months.In the plain areas of harvesting, will be from November to January.Hillside will be from January to March. Pods when they becomeOrange-red colour are harvested. During harvest, do not apply any chemicals on red ant. When the pepper turns from green to reddish yellow, that time all the strings have to be harvested.
Well matured unripe fruits should be harvested.Harvesting should be in the hands.Harvested tenders should be kept in aluminium bowl with a hole or in bamboo baskets. Dip it in the 80 centigrade boiling water, and then dried in the sun for 7-10 days and turns it back and front to have the occasional deflecting. If back pieces does not turned,
caused by fungal growth.The cleaning water should be used and should be macarrum.
Yield :
From 2 to 3 kg of dried pepper in one vine a year.
Benefits of pepper tender, put in hot water The tenders which has boiled in hot water, it takes 3-4 days for dry. The time will be saved. Dry peppers found in the same dark color.
White pepper:
To produce white pepper, the well matured 3 to 5 pods should be harvested. Pods that not matured to extract alone. Then the mature fruits should be keeping ripe in a gunny bag up to 1-2 days. 50 kg gunny bags with the mature fruits, must be tied loosely. After that these bags are diped in the canal upto 69 days. Keeping the outer peel to keep up.
After taking out the bags, to extract the pieces apart. And wash it and dry. To dry these pods, to spread it in cement or on bamboo mats.Heap continues, spreading the same model again in 2-hour intervals to keep dry. Dry it until 11% moisture and packed in clean poly (or) gunny bag.
For more details
Professor and Head
Horticultural Research Station
vijayanagaram, Ooty - 643 001.
Phone - 0423-2442170
Email - hrsooty@tnau.ac.in |
|
|

