OBESITY
Obesity is a state in which there is a generalized accumulation of excess fat in adipose tissue in the body leading to more than 20% of the desirable weight. The size and number of fat cells increase in obese people. A person is said to be obese when the body weight is 20% or more above ideal body weight, which can be calculated by comparing his height and sex. In recent years obesity has become a public health problem of considerable importance in India and all over the world.
1. CAUSES OF OBESITY
2. ASSESSMENT OF OBESITY
3. COMPLICATIONS OF OBESITY
4. PREVENTIVE MEASURES
5. DIETARY GUIDELINES
6. TIPS TO REDUCE WEIGHT
Obesity is the most common nutritional disorder in infants, children and adults and leads to more health problems than all the vitamin deficiencies.
The importance of obesity requires constant emphasis, not only because of excess mortality it causes, but also because of numerous complications and the predisposition it creates to common and potentially serious conditions such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension and cardiovascular diseases.
It is frequently associated with emotional and other physiological disturbance, all of which may interfere in a major way with the welfare of the individual, the family, the community and even the nation.
1. CAUSES OF OBESITY
Top
-
Heredity
-
Social and cultural factors.
-
Emotional factors.
-
Obesity due to malfunctioning of some, one or more of the endocrine glands i.e. thyroid.
-
Excessive food intake
-
Sedentary life style.
-
Intake of certain drugs.
2. ASSESSMENT OF OBESITY
Top
There are many scientific methods to assess the amount of body fat and diagnose obesity, but these methods need some instruments or laboratory techniques. So here we have listed some relatively simple methods to assess obesity.
-
A very simple method of assessing obesity is done by weighing the person. By simple weighing, obesity is diagnosed if the weight is in excess of the average desirable weight for men and women at a given height. It is also important to measure the height accurately.
-
Body mass index (BMI) is the most commonly used criterion to diagnose obesity. It was described by Quetelet and is also called Quetelet Index.
It is calculated as,
Weight (kg)
Body mass index (BMI) = ------------
Height (m2)
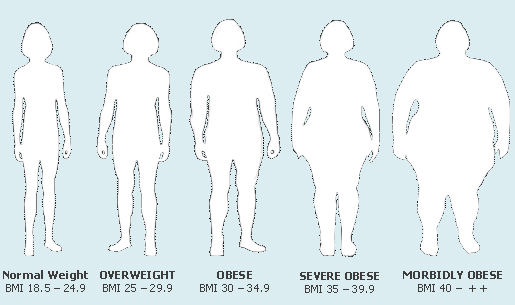
On the basis of BMI, Obesity is graded as follows,
BMI in adults (men and women)
Category |
Kg/m2 |
Normal:
Obesity:
Grade I
Grade II
Grade III |
19-24
25-29
30-40
above 40 |
A variety of other anthropometric measurements have been employed in the diagnosis of obesity. The waist hip ratio is a simple and fairly useful parameter. In man, fat tends to be deposited more on the chest and the abdomen, while in women the tendency for fat deposition is more on the buttocks and thighs. For men a waist-to-hip ratio above 1.0 and for women a waist–to–hip ratio above 0.9 indicate obesity.
Waist circumference (cm)
Waist-to-hip ratio= -------------------------------
Hip circumference (cm)
3. COMPLICATIONS OF OBESITY
Top
Obesity leads to the development of several complications such as
-
Physical disabilities
-
Metabolic disorders
-
Cardiac disorders
-
Proneness to accidents
-
Low life expectancy
Obese persons suffer more often from metabolic disorders such as diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis and heart diseases. They meet with accidents more frequently. The life expectancy is also reduced in view of the above hazards.
4.PREVENTIVE MEASURES
Top
-
Diet control
-
Exercise
-
Doing household activities (washing clothes, fetching water, cleaning the house etc.)
-
Avoid unnecessary intake of drugs (eg: tablets for preponing and postponing menstruation, oral contraceptives.)
By using all these methods reduce weight gradually. If the rate of weight reduction slows down do not worry. Continue the exercise and food restriction which will bring about weight reduction is due course. Maintenance the reduced body weight is essential for the upkeep of the improved health condition.
5. DIETARY GUIDELINES
Top
A. FOODS TO BE AVOIDED
i. Calorie rich foods
-
Sweets
-
Bakery products
-
Carbonated beverages
-
Roots and tubers
-
Egg yolk
ii. Fat rich foods
-
Fried foods
-
Fast foods
-
Cheese, butter, ghee, ice cream etc.
-
Cakes with icing
B. FOODS TO BE RESTRICTED
-
Cereals
-
Pulses
-
Milk
-
Eggs
-
Flesh foods
C. FOODS TO BE TAKEN LIBERALLY
-
Vegetables
-
Green leafy vegetables.
SUGGESTED RECIPES
Food |
Reason |
Vegetable salads
Chapattis without oil
Steamed foods like idlis, idiyappam etc.
Thin soups
Poached fish
Greens poriyal
Coffee or tea without sugar |
Low calorie and high fibre.
More protein and high fibre and give satiety.
To limit calories, increase protein content.
Provide fluids, low calorie value, provide fullness.
Low in calories, high in good quality protein.
High in fibre, vitamins and minerals.
Low calorie. |

6. TIPS TO REDUCE WEIGHT
Top
-
Eat less fried foods.
-
Eat more fruits and vegetables.
-
Eat more fiber rich food items like whole grains, grams and sprouts.
-
Do regular exercise to keep the body weight within normal limits.
-
Slow and steady reduction in body weight is advised.
-
Severe fasting may lead to health hazards.
-
Enjoy a variety of foods needed to balance your physical activity.
-
Eat small meals regularly at frequent intervals.
-
Cut down sugar, fatty foods and alcohol.
-
Use low-fat milk.
-
Weight reducing diet must be rich in protein and low in carbohydrate and fat.
FOODS TO BE INCLUDED |
 |
 |
FOODS TO BE AVOIDED |
 |
 |
PHYSICAL ACTIVITY |
AVOID UNNECESSARY INTAKE OF DRUGS |
|
 |
Source
Srilakshmi .B 2003.Dietetics, New Age International (P) Publishers Ltd.Chennai.
Vijayapushpam et al. 2008, Beware of obesity. NIN, Hyderabad.
http://www.newsmotion.com/sitebuildercontent/sitebuilderpictures/alert_chart.gif
http://doctor.ndtv.com/topicsh/Obesity.asp
http://www.obesityindia.in/images/obesity_chart.gif
http://www.torch.aetc.af.mil/AFG-070503-014.jpg
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus /19811.jpg
http://chickenfriedyankee.files.wordpress.com/2008/04/55206748_61cdf01533.jpg
http://www.dkimages.com/discover/previews/1101/10446126.JPG
http://www.growingyourownveg.com/sites/fruits_and_vegetables2%5B1%5D.jpg
http://www.diamondorganics.com/images/ |









