FOOD REQUIREMENTS AND ADEQUATE DIETS FOR VULNERABLE GROUPS
The requirement of the body for the various nutrients carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals depend on age, sex, physical work and other physiological conditions. A manual labourer engaged in heavy work requires more proteins, calories and minerals per kg of his body weight than an adult. Pregnant women and nursing mothers require more calories, proteins, minerals because of the physiological changes that take place during this period. The Nutrition advisory committee of ICMR has made recommendations of nutrients
Energy
The body needs energy to maintain body temperature for metabolic processes to support growth, for functioning of the internal organs such as heart, kidney, lungs etc and for physical activity. Energy needs are influenced by factors such as body size, age, climate, extent of physical activity and altered physiological status such as pregnancy and lactation.
Energy allowance for infants
| Age |
Kcal/Kg |
3 months
3-5 months
6-8 months
9-11 months
Average during 1st year |
120
115
110
105
112 |
Recommendation of energy intake of infants is based on breast milk intake. These allowances would form guidelines in feeding children who do not get sufficient breast milk. Usually the breast milk would be sufficient to meet the calorie recommendation up to 5-6 months and later require supplementation with other food stuffs besides milk in order to fulfill not calories but also other nutritional requirements.
Age group |
Body weight
(kg) |
Energy allowance
(K cal) |
1-3 years
4-6 years |
12.03
18.87 |
1220
1720 |
The allowances for calories are based on ideal body weight and not on actual body weights.
Energy allowances for Adults
Recommendation for adults is made on a “Reference man” and “Reference women” who belong to the age group 20– 39 years and weighing 55 kg and 45 kg respectively.
Energy allowances for women performing moderate activity
| Category |
Energy allowance (kcal) |
Women (Normal)
Pregnancy
Lactation (1st 6 months)
6-12 months |
2200
2500
2750
2600 |
During pregnancy additional energy is needed to support the growth of the foetus, placenta, maternal tissues as well as to meet the increased metabolic rate. 300 extra calories is provided during pregnancy. Extra energy is provided during lactation for encouraging optimum secretion of milk. During the 1st 6 months the quantity of milk produced by the mother is more and an extra allowance of 550 kcal is made during this period. Since women continue to lactate beyond 6 months, with reduced milk output up to one year, an extra allowance of 400 kcal/day recommended for periods from 6-12 months.
Proteins
Proteins are needed for building and repairing of body tissues, muscles and vital fluids like blood to help enzymes and anti-bodies to fight infections. Protein requirements are based upon actual estimation of the lowest amount of nitrogen intake necessary to maintain nitrogen equilibrium and have been evolved by N balance studies. Protein requirements are expressed in terms of body weight. In a diet with energy deficiency, some of the protein would be burnt or wasted in providing energy and will not be available for the synthesis of body protein. The efficiency with which protein is utilised, also decreases.
Energy allowance for infants
Age |
Protein allowance
per day g/kg |
0-3 months
3-6 months
6-9 months
9-12 months |
1.3
1.8
1.8
1.5 |
Allowances for infants should be made for the rapid growth. The allowances for the first 6 months are met by milk proteins. Later the child has to be supplemented with other sources of protein.
Age group |
Body weight |
Protein allowances |
g/kg/day |
g/day |
1-3 years
4-6 years |
12
19 |
1.8
1.6 |
22
29 |
Protein allowances during pregnancy and lactation
Allowance for pregnant women must cover the additional needs for the development of the foetus, placenta and material tissues, while those of lactating women must cover what is secreted in milk. During the 2nd and 3rd trimester an extra allowance of 14g/day have been made. During the first 6 months of lactation an extra allowance of 25 g/day have been made. This is over and above the normal protein requirement of 45 g/day.
Minerals
Iron
Iron is an important constituent of haemoglobin, myoglobin and several enzymes. The widespread prevalence of iron deficiency anemia despite sufficient iron intake in our Indian diet suggests that factors other than low intakes of iron are concerned with the development of iron deficiency anaemia. These may be due to either excessive iron loss or very poor bio-availability of dietary iron or both. Recommended intake of iron is calculated on the basis of iron loss and iron absorbed from diets which is around 3 percent in man and about 5 percent in women. Cereal based Indian diets have high phytate content which interferes with the absorption of iron. Tannin in food also renders iron unavailable, calcium and vitamin – C improve dietary absorption.
Recommended allowance for Iron
Group |
Iron requirement mg/day |
Dietary intake mg/day |
Rate of absorption % |
Infants
Children
Adolescent girls
Women (normal)
Pregnancy
Lactation |
1.0 mg/kg
0.65
1.7
1.6
3.4
1.6 |
-
20.25
35
32
40
32 |
-
2
3
5
8
5 |
Calcium
Most of the calcium in the body is present in the skeletal structure. Calcium has a role in neuromuscular excitability, blood coagulation and membrane permeability.
Recommended allowance
| Group |
Calcium allowance mg/day |
Infant
Children 1-6
Women (normal)
Women (Pregnant/Lactation) |
500-600
400-500
400-500
1000 |
Vitamins
Vitamin A is essential for normal vision, for maintaining the integrity of epithelial tissue and for a wide variety of metabolic functions. Vitamin A in the human diet either exists as preformed vitamin A (retinol) as beta carotene which in the body is converted to vitamin A. Only foods of animal origin contain vitamin A. All vegetable sources contain B carotene and considering various factors influencing the conversion into retinol, a conversion factor of 0.25 may be used.
Vitamin C has a role, in the synthesis of collagen, wound healing amino acid, iron and carbohydrate metabolism and synthesis of hormones. This vitamin is destroyed by oxidation during storage and cooking at high temperature.
Recommended allowance for Vitamin A and C
Group
|
Vitamin A
mg/kg |
Retinol
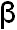 -carotene µg/100g -carotene µg/100g |
Vitamin C
mg |
Infants 0-6 months
6-12 months |
400
300 |
-
1200 |
20
20 |
Children 1-3 years
4-6 years |
250
300 |
1000
1200 |
40
40 |
Women (normal)
Pregnancy
Lactation |
750
750
1150 |
3000
3000
4600 |
40
40
80 |
Dos and don’ts during pregnancy
-
Eat more food during pregnancy and lactation.
-
An additional meal is preferable.
-
Eat more whole grain, sprouted grams and fermented food.
-
Take milk/meat/egg.
-
Eat plenty of vegetables, green leafy vegetables and fruits.
-
Do not use alcohol and tobacco.
-
Take medicine only when prescribes.
-
Take iron, folate and calcium supplements regularly after 14-16 weeks of pregnancy and continue the same during lactation.
-
Beverages like tea and coffee bind dietary iron and make it unavailable, hence they should be restricted before and soon after a meal.
-
Pregnant women need walking and other physical activity and should avoid heavy physical work, particularly during the last month of pregnancy.
ADOLESCENT GROWTH SPURT
Adolescents constitute more than one-fifth of Indians population. The word “Adolescent” comes from latin word ‘Adolescere’ meaning to grow, to mature signifying the special features of adolescence.
Growth, development and nutrition
Adequate nutrition is critical for growth spurt during adolescence. Poor nutrition is often cited as one of the reasons for delay in the onset of puberty, especially among Indian adolescent girls. Growth spurt which signals the onset of puberty depends on the girls attaining a critical body composition of 10% body fat.There is increased demand for energy, protein, minerals and vitamins during adolescence.
Group |
Particulars |
Net energy
Kcal/d |
Protein
g/d |
Visible fat
g/day |
Calcium
mg/d |
Iron
mg/d |
Vitamin mg/kg
(b carotene) |
Boys |
10-12 years |
2190 |
54 |
22 |
600 |
34 |
2400 |
Girls |
10-12 years |
1970 |
57 |
19 |
Boys |
13-15 years |
2450 |
70 |
22 |
600 |
41 |
2400 |
Girls |
13-15 years |
2060 |
65 |
28 |
Boys |
16-18 years |
2640 |
78 |
22 |
500 |
50 |
2400 |
Girls |
16-18 years |
2060 |
63 |
30 |
Source
Sriramachandrasekharan, M.V and Ravichandran, M. 1999. Principles of Human Nutrition. Lotus Publishers, Tirunelveli.
Vijayapushpam et al. 2008, Adolescent Growth Spurt. NIN, Hyderabad. |
