| Fruit borer |
Symptom of Damage
- Bolls showing regular, circular bore holes
- Larvae seen feeding on the boll by thrusting their heads alone inside and leaving the rest of the body outside
- Presence of granular faecal pellets outside the bore hole.
- A single larva can damage 30-40 bolls.
|
 |
 |
| Feeding injury |
Circular bore hole |
 |
 |
Identification of pest
Scientific Name - Helicoverpa armigera
- Eggs - Spherical in shape and creamy white in colour, present singly
- Larva - Shows colour variation from greenish to brown.
- It has dark brown grey lines on the body with lateral white lines and also has dark and pale bands.
- Pupa - Brown in colour, occurs in soil, leaf, pod and crop debris
- Adult
- Light pale brownish yellow stout moth.
- Forewings are olive green to pale brown in colour with a dark brown circular spot in the centre.
- Hind wings are pale smoky white with a broad blackish outer margin.
|
| Eggs |
Larva |
 |
 |
| Pupa |
Adult |
Management Strategies
| |
- Avoid continuous cropping of cotton both during winter and summer seasons in the same area as well as ratooning.
- Avoid monocropping. Growing of less preferred crops like greengram, blackgram, soyabean, castor, sorghum etc., along with the cotton as intercrop or border crop or alternate crop to reduce the pest infestation.
- Removal and destruction of crop residues to avoid carry over of the pest to the next season, and avoiding extended period of crop growth by continuous irrigation.
- Judicious water management for the crop to prevent excessive vegetative growth and larval harbourage.
- Application of Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus (NPV) at 3 x 10 12 POB /ha in evening hours at 7th and 12th week after sowing.
- Inundative release of egg parasitoid, Trichogramma spp., at 6.25 cc/ha at 15 days interval 3 times from 45 DAS
- Releasing predator Chrysoperla carnea @ 1, 00, 000/ha at 6th, 13th and 14th week after sowing.
|
|
| Top |
| Pink bollworm |
 |
|
Symptom of Damage
- Rosetted flowers
- The holes of entry plugged by excreta of larvae which are feeding inside the seed kernels.
- They cut window holes (interlocular burrowing) in the two adjoining seeds thereby forming "double seeds"
- The attacked buds and immature bolls drop off.
- Discolored lint and burrowed seeds.
|
|
|
Identification of pest
Scientific Name - Pectinophora gossypiella
Larva
- Shows colour variation young larva white and late instar almost black, brown or green to pale or pink
- several dark and light alternating bands running the entire length
Adult
- Small moth.
- Forewings arebrown or dull yellow olive grey with dark spots on the forewing.
- Hind wings margins are deeply fringed.
|
 |
|
| |
| |
| |
Management Strategies
|
|
- Clean cultivation and destruction of crop residues (fallen leaves, twigs etc.) before the onset of season.
- Plough deeply to expose the hibernating larvae / pupae.
- Avoid late sowing of the crop. Early sowing helps in early maturity facilitating escape.
- Withholding irrigation water to avoid prolonged late boll production/ formation to reduce the build up of over-wintering population.
- Acid delinting of cotton seeds.
|
|
| Top |
| Spotted bollworms |
Symptom of Damage
- Drying and drooping of terminal shoots during pre –flowering stage
- Shedding of squares and young bolls
- Flaring up of bracts during square and young boll formation stage
- Holes on bolls and rotting of bolls.
|
 |
 |
| Drying - terminal shoots |
Bore holes and rotting |
 |
|
| Flared square |
|
 |
 |
Identification of pest
Scientific Name - Earias vittella
- Larva : Brownish with white streaks dorsally and pale yellow ventrally, Without finger shaped processes.
- Adult
- Small buff coloured. 0
- Forewings are pea green with a wedge shaped white band running from base to out margin.
Scientific Name - Spiny bollworm: Earias insulana
- Larva : Brown with dorsum showing a white median longitudinal streak.
The last two thoracic segments and all the abdominal segments have two pairs of fleshy tubercles (finger shaped processes) one dorsal and the other lateral
- Pupa - Brown and boat shaped
- Adult - Small buff coloured. Forewingsare uniformly silvery green
|
| E. vitella - Larva |
E. vitella - Adult |
 |
 |
| E. insulana - Larva |
E. insulana - Adult |
Management Strategies
- Collect and destroy all the shed fruiting parts
- Planting trap crop of bhendi, uprooting and burning
- Don't extend the crop period.
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
| Top |
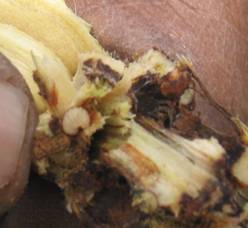
| Cotton Stem Weevil |
 |
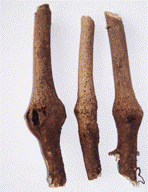 |
Symptom of Damage
- Swellings on the stem just above the ground level.
- Young plants are invariably killed
- Older plants that survive, lack vigor and strength, and when strong winds blow, these plants sometimes break at the nodes.
Identification of pest
Scientific Name - Pempheres (Pempherulus) affinis
- Larva : Grub, white in colour without leg (apodous)
- Adult : Very small weevil, dark in colour with two small white patches on the elytra
Management Strategies
- Basal application of FYM 25 t/ha or 250 kg/ha of neem cake.
|
| Stem gall |
Stem galls |
 |
|
| Grub |
|
| Top |
| Shoot weevil |
Symptom of Damage
- Plants with drooping leaves,
- Wilting in patches
Identification of pest
Scientific Name - Sphennoptera gossypii
- Adult - Dark brown jewel beetle
Management Strategies
- Basal application of FYM 25 t/ha or 250 kg/ha of neem cake.
|
 |
 |
| Affected stem |
Infested plants |
| |
|
|
| Top |
| Leaf roller |
 |
 |
Symptom of Damage
- Leaves rolled in the form of trumpets fastened by silken threads
- Marginal portion of leaves eaten away
- Plants defoliated in severe attack
Identification of pest
Scientific Name - Sylepta derogata
- Larva - Bright green (glistening) with dark head and prothoracic shield.
- Adult - Moth with yellow wings having brown wavy markings
Management Strategies
- Collection and destruction of sheded plant parts.
- Hand picking and destruction of grown up caterpillars.
|
| Rolled leaves |
Larva |
 |
|
| Adult |
|
| |
|
|
| Top |
| Tobacco Cutworm |
Symptom of Damage
- Scrapping the epidermal layer, leaving the skeleton of veins of leaf
- During severe attack, only the stem and side shoots will be standing in the field without any leaf or bolls
- Larvae feed the leaves by making small holes
Identification of pest
Scientific Name - Spodoptera litura
- Egg - Laid in masses which appear golden brown
- Larva - Pale greenish with dark markings.
- Gregarious in the early stages
|
 |
 |
Management Strategies
- Use of light trap
- Set up the sex pheromone trap Pherodin S.L. at 12/ha
- Growing castor along border and irrigation bunds.
- Removal and destruction of egg masses in castor and cotton crops.
- Removal and destruction of early stage larvae found in clusters
- Collection and destruction of sheded plant parts.
- Hand picking and destruction of grown up caterpillars.
|
|
| Top |
| Cotton aphid |
| |
|
Symptom of Damage
- Infesting tender shoots and under surface of the leaves.
- Curling and crinkling of leaves
- Stunted growth
- Blighted appearance when infestation is severe
- Development of black sooty mould due to the excretion of honey dew giving the plant a dark appearance
Identification of pest
Scientific Name - Aphis gossypii
- Nymphs - Yellowish or greenish brown found on the undersurface of leaves.
- Adults - Greenish brown, soft bodied and small insects.
- Winged forms may be seen under crowded conditions.
Management Strategies
- Monitoring the activities of the alate adult by setting up yellow sticky traps
|
 |
 |
| |
|
 |
|
|
| Top |
| Thrips |
Symptom of Damage
- Shriveling of leaves due to scrapping of epidermis and desapping
- Attacked terminal buds – have ragged edges
- Silvery shine on the undersurface of leaves
Identification of pest
Scientific Name - Thrips tabaci
- Nymphs - Very minute, slender, yellowish and microscopic
- Adult - Small, slender, yellowish to brown with fringed wings
|
 |
 |
Management Strategies
- Monitor the nymphs and adults of early season sucking pests from the 14th day after sowing.
|
|
| Top |
| Whitefly |
 |
 |
Symptom of Damage
- Chlorotic spots on the leaves which latter coalesce forming irregular yellowing of leaf tissue which extends from veins to the outer edges of the leaves
- Severe infestation results in premature defoliation
- Development of sooty mould
- Shedding of buds and bolls and poor boll opening
- It also transmits the leaf curl virus diseases of cotton.
Identification of pest
Scientific Name - Bemisia tabaci
- Nymph - Greenish yellow, oval in outline,
- Pupa - Puparia oval in shape, present on the under surface of the leaves.
- Adult - Minute insects with yellow body covered with a white waxy bloom.
|
| Nymphs |
Adult |
Management Strategies
- Growing cotton only once a year either in winter or summer season
- Adopting crop rotation with non-preferred hosts such as sorghum, ragi, maize etc.,
- Removal and destruction of alternate weed hosts like Abutilon indicum, Chrozophore rottlari, Solanum nigrum
- Timely sowing with recommended spacing
- Late sowing may be avoided and the crop growth should not be extended
- Field sanitation may be given proper attention.
- Cultivation of most preferred alternate host crops like brinjal, bhendi, sunflower may be avoided
- Set up yellow pan traps and sticky traps @ 12/ ha
- Collection and destruction of whitefly infested leaves from the plants
|
|
| Top |
| Red cotton bug |
Symptom of Damage
- Red stained lint and rotting bolls.
- Inner boll wall with warty growth or water soaked spots
- Young bolls abort and turn dark brown
- The bacterium Nematospora gossypii enters the site of injury and stains the fibre
Identification of pest
Scientific Name - Dysdercus cingulatusi
- Nymphs and Adults - Reddish bugs with white bands on the abdomen and black markings on the wings
|
 |
|
Management Strategies
- Plough the field to expose the eggs.
- Spray phosphamidon 100 EC@250 ml/ha
|
|
| Top |
| Mealy bugs |
Symptom of Damage
- Heavy clustering of mealy bugs usually seen under surface of leaves as a thick mat with waxy secretion.
- Excrete copious amount of honey dew on which the fungus sooty mould grow.
- Affected plants appear sick and black, resulting reduced fruiting capacity.
Management Strategies
- Control of weeds and ratoon cotton
- Avoid planting on poorly drained soil
|
 |
 |
| Infested plants |
Mealy bugs on stem |
|
| Top |

