PEST MANAGEMENT
Shoot and fruit borer (Earias vittella, E. insulana)
|
|
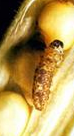
This is also one of the common pests in cotton and attacks a large number of malvaceous plants. Infestation and damage to crops is more in summer. The insect is distributed widely throughout India.
Life cycle : The total life cycle of the insect is completed in 30–40 days. The adult moths are about 13–15 mm with a pale brownish white head and thorax. The hind wings are creamy white in colour. In E. vittella, the forewings are pale white with a broad, wedge-shaped horizontal green band in the middle whereas in E. insulana the forewings are uniformly green in colour. Eggs are spherical with longitudinal ridges, single and light bluish green in colour. They are laid singly on buds, flowers, fruit or on shoot tips. The larvae are stout, brown in colour with white markings. The pupae are found in inverted boat shaped silky cocoons.
Symptoms
The larvae bore into tender shoots and move downwards, creating a tunnel inside. The growing points are affected and hence side shoots may arise. The affected shoots wither and droop. The caterpillars also bore into the buds, flowers and fruits and feed on the inner tissues. The damaged flowers fall off and the affected pods are malformed.
Economic threshold level :
The economic threshold level is 10% damage to the crop.
Management
- Sowing in the first week of June is ideal to avoid damage of shoot and fruit borer during the rainy season.
- Summer ploughing should be done to destroy bollworm pupae.
- Spray ginger, garlic, chili or Sida acuta kashayam.
|
 |
  |
  |
Leaf hoppers (Amrasca biguttula biguttula)
|
|
This is a polyphagous pest found widely infesting okra, cotton, brinjal, castor, beans and cucurbits.
Life cycle
The adults are 2 mm in size, wedge-shaped, pale green in colour with two black spots on the vertex and a single black spot on the posterior half of each forewing. The nymphs are translucent and yellowish green in colour. They insert their eggs into the tissues of the veins on the under surface of the leaves.
Symptoms
The nymphs and adults suck the sap from the under surface of the leaves and inject toxic saliva into the plant tissues. The affected leaves first turn yellow, then brick red, before they become brittle and fall off. In cases of severe infestation, the fruits are also affected. Climatic factors like cloudy weather play an important role in population build up. Heavy showers wash off the nymphs and adults.
Economic threshold level : The economic threshold level is the presence of one to two nymphs or adults per leaf.
Management
- Install yellow sticky traps @ 30/ha • Spray 5% neem seed kernel extract or ginger, garlic, chili extract or Sida acuta extract.
|
|
Fruit borers (Helicoverpa armigera, Spodoptera litura)
|
|
Life cycle
The eggs are yellowish white in colour. The caterpillars are of varied colours, mostly dark greenish brown or apple green. They have whitish or dark grey longitudinal lines with white stripes on the lateral side. The adult moths are medium sized, stout and pale brownish in colour. The forewings are pale brown in colour. They have indistinct wavy lines along the margin with a dark brown spot at the centre. The hind wings are smoky white in colour with a blackish outer border. The pest completes about four generations in a year. Eggs are yellowish-white in colour and dome-shaped. The eggs laid in the leaf buds hatch in 2–5 days. The larvae pass through six instars. When the larvae are fully grown, they burrow into the soil to a depth of 2–18 cm for pupation. The pupae are smooth, 14–18 mm long. The pupal period lasts for 5–8 days.
Damage pattern
The larva feed on the foliage. When the tender leaf buds are infested, symmetrical holes or cuttings are seen when unfolded.
Management
- Adopt summer ploughing to destroy bollworm pupae. • Place 15–20 bird perches per hectare. This invites predatory
birds
- Mix one kilogram of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum)
flour with two litres of water and keep aside for 24 hours. Then add 40 litres of water to the mixture and spray in one- hectare area. This ensures fifty percent control within seven days.
- Prepare an herbal pesticide by boiling 4 kg of aloe (Aloe vera), 500 ml of neem oil and 500 gm of tobacco powder in 20 litres of water. Boil the contents for 3–4 hours until it reduces to one-fourth of the original volume. Allow it to cool, add 50 gm of soapnut (Sapindus emarginatus) seed powder and mix thoroughly. Dilute 100–150 ml of this filtrate in 15 litres of water and spray.
- Install pheromone traps @ 8 per hectare.
- Spray 5% neem seed kernel extract or Andrographis kashayam or five leaf extract to kill early stages of the larvae
- Use biocontrol agents like Trichogramma @ 50,000 eggs/ha six times at weekly intervals.
|
Other minor pests
|
|
- Aphids – Aphis gossypii
- Thrips – Thrips tabacii
- Red cotton bug – Dysdercus cingulatus
- Leaf rollers – Sylepta derogate
|
|
Beneficial insects
|
|
| Crickets, ants, wasps, ladybird beetles |
|
Source : Centre for Indian Knowledge Systems, Chennai
Updated on : Dec 2014 |

