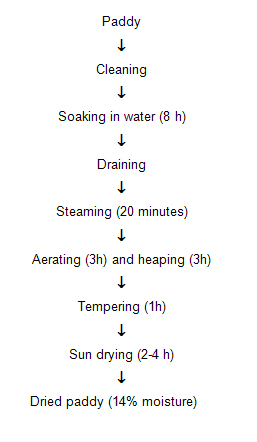
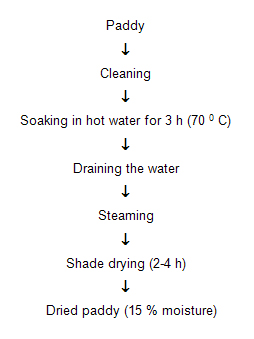
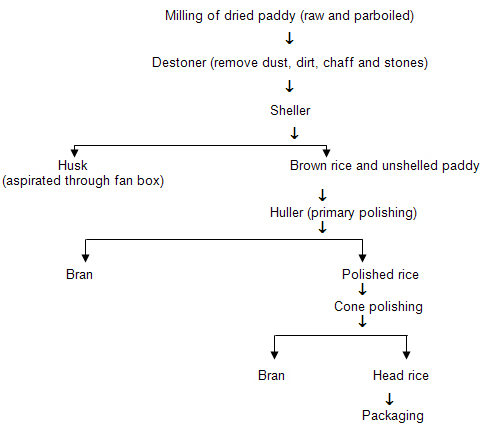
Parboiling
Parboiling is a hydrothermal treatment followed by drying before milling for the production of milled parboiled grain. Parboiling of paddy has been known in the orient for centuries. Nearly 50 per cent of the paddy produced in India at present is parboiled.
In general, the three major steps in parboiling, i.e. soaking, steaming and drying and have a great influence on the final characteristics and quality of parboiled rice.
Parboiling is the latest premilling treatment which improves the quality of rice. The traditional parboiling process in India is carried out in different ways. |