|
Coffee (Coffea canephora / Coffea arabica)
Rubiaceae |
|
|
|
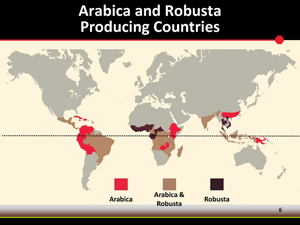 |
| World - Coffee Production Map |
|
|
| Coffee Plantation |
 |
 |
|
|
| Varieties |
| Arabica varieties |
Sln 795, Sln 7, Sln 9, Sln 10, Cauvery and its selections and HRC (Hawaian Red Cuturra), Chandragiri and san Roman
|
Robusta varieties
Sln 274, Sln 270, Sln 3.
|
| Varieties |
Parentage |
Special characters |
Selection 1 (S288) |
Tetraploid hybrid from S26 (natural cross – C. liberica x C. arabica) |
Resistance to leaf rust race 1 & 2, high yielding. Wider adaptability |
Selection 3 (S795) |
Cross between S.288 x Kent |
Resistance to leaf rust race 1 and 2, 700 -1200kg/ha
Bold fruits 75% A grade |
Selection 5 |
Devamachy x S -881 |
Small, oblong fruits 900 – 1100kg/ha |
Selection 6 z |
S-274 (Robusta) x Kents |
High A grade beans, 900 – 1000kg/ha |
Selection 7 |
San Ramon –a short internode arabica |
Dwarf in stature, segregates to tall by 30% |
Selection 8 |
Pure line selection of Hibrido –de -Timor |
Highest resistance to leaf rust, drooping branches |
Selection 9 |
Sln 8x Tafarikela |
Drought hardy, suitable to different coffee zones |
| Selection 10 |
Double cross hybrid, Cattura x( S795 XHDT) |
Resistant to leaf rust |
| Selection 11 |
Progency of C.liberica X c.eugenoides |
Field resistance to rust and drought hardiness |
| Cauvery |
Catimor x Hibrido de Timor |
Plants are dwarf, suitable for high density planting
Yield – 3000kg/ha
More a grade beans with superior cup quality |
| Selection 12 |
Cross Caturra x HDT, followed by selfing |
Precocious, suitable for close planting, resistant to leaf rust |
|
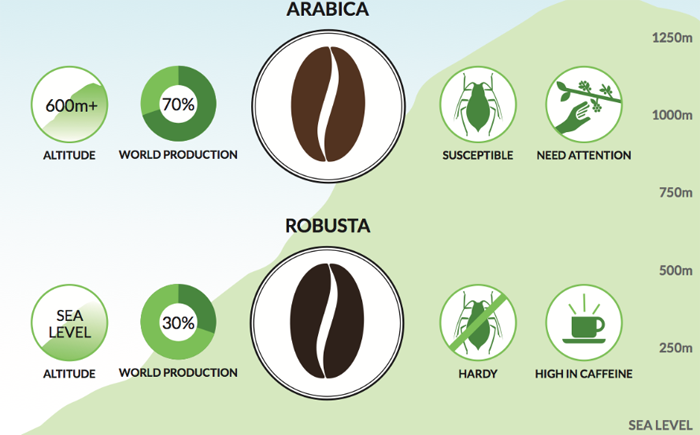
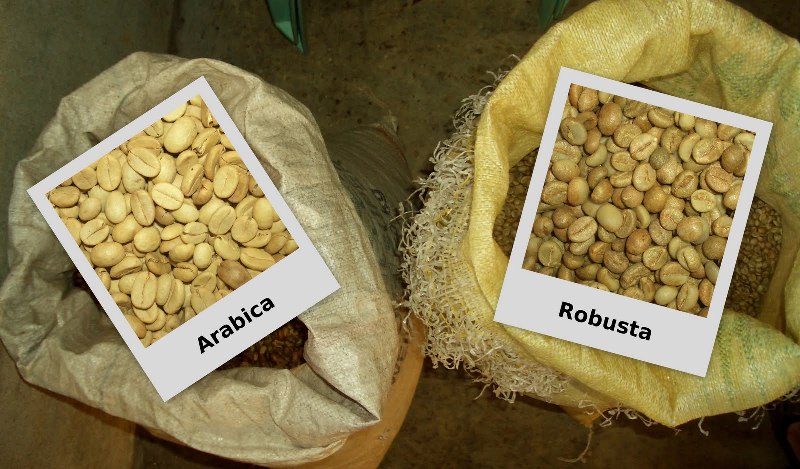
| Arabica Vs Robusta |
|
 |
|
Soil and climate
Soil should be deep, friable, open textured rich in plant nutrients with plenty of humus and of slightly acidic nature (pH – 4.5 to 6.5)
| Varieties |
Elevation (m) |
Rainfall (mm) |
Distribution |
| Robusta |
500 – 1000 |
1000 - 2000 |
Blossom shower – February - March |
| Arabica |
1000 - 1500 |
1600 - 2500 |
Blossom shower – March - April |
| Backing shower during April – May is required for both the varieties |
|
Seeds and sowing
Coffee is propagated by seeds
Season
Planting spreads from June - December
Preparation of seeds
Healthy and well developed fully ripe berries are harvested from specially identified plants for use as seed bearers. After discarding the floats, the sound fruits are depulped, sieved and mixed with sieved wood ash and dried in shade. The seed is then graded to remove all cut, triangular and elephant beans. Prior to planting, the seeds are treated with Agrosan or any Organomercurial compound to prevent fungal infection.
Nursery practices
Select light loamy soil of good drainage with high organic matter content with water and shade facilities. Form raised beds of 15 cm height, 1m width and at convenient length. Incorporate 30 - 40 kg of well rotten compost, 2 kg of finely sieved agricultural lime and 400 g of rock phosphate to a bed of 1 x 6 m size. In heavy soils, it is necessary to add coarse sand for drainage and aeration. |
 |
|
Sowing
Pre-sowing seed treatment
wiith Azospirillum and Phosphobacterium can be done.Seeds are sown in December - January in the bed 1.5 - 2.5 cm apart with the flat side down wards in regular rows.
Then they are covered with a thin layer of fine soil and a layer of paddy straw.Water the beds daily and protect from direct sunlight by an over head pandal.
Seeds germinate in about 45 days after which they are transplanted to a secondary nursery beds for raising ball or Bag nursery.
Bag nursery
Polythene bags with adequate number of holes in the bottom half are taken and are filled with a prepared mixture containing jungle soil, FYM and sand in the proportion of 6:2:1. An area of 12 x 8 m can accommodate 5000 seedlings. Seedlings are planted in polythene bags.
Preparation of field
Selective felling may be done while retaining a number of desirable shade trees. Terracing should be done in deep slopy areas. After the summer showers, pits of 45 cm x 45 cm x 45 cm are dug at 1.25 - 2.5 m apart. The pits are left open for weathering and then filled and heaped for planting. At the time of filling, apply 500 g of rock phosphate per pit along with top soil. Planting is done along the contour in slopy areas.
Spacing
| Arabica Coffee |
: |
1.5 to 2.0 m either way.
|
| Dwarf varieties |
: |
Sanraman: 1 x 1 m. |
| Robusta coffee |
: |
2.5 m either way. |
|
 |
| Shade Tree |
|
 |
Planting shade trees
Dadap is commonly used as a lower canopy shade. Two metre long stakes are planted for every two plants of coffee. Silver Oak and Dadaps are planted during June when rains of South-West monsoon commences. During summer the stem of young Dadaps are painted with diluted lime or wrapped in agave leaves or polythene sheets in order to prevent them from sun scorch. Regulate shade by cutting criss-cross branches during monsoon season. Silver oak trees are planted for permanent shade.
Irrigation
It is generally grown as a rainfed crop. But irrigation with sprinkler during March - April increases blossoming and results in higher yields. |
|
Manuring
Species |
Pre- Blossom March
N:P2O5:K2O |
Post – blossom May
N:P2O5:K2O |
Mid monsoon
August
N:P2O5:K2O |
Post- monsoon
October
N:P2O5:K2O |
Total |
| Arabica |
| Young coffee 1st year after planting |
15:10:15 |
15:10:15 |
--- |
15:10:15 |
45:30:45 |
| 2nd and 3rd year |
20:10:20 |
20:10:20 |
--- |
20:15:20 |
60:45:60 |
| 4th year |
30:20:30 |
20:20:20 |
--- |
30:20:30 |
80:60:80 |
Bearing coffee 5 years and above for less
than one tonne/ha crop |
40:30:40 |
40:30:40 |
--- |
40:30:40 |
140:90:120 |
| For one tonne / ha and above |
40:30:40 |
40:30:40 |
40:30:40 |
40:30:40 |
160:120:160 |
| Robusta |
| For less than one tonne/ ha crop |
40:30:40 |
--- |
--- |
40:30:40 |
80:60:80 |
| For 1 tonne /ha and above |
40:30:40 |
40:30:40 |
--- |
40:30:40 |
120:90:120 |
Aftercultivation
Weeding and mulching should be done as and when necessary. Digging is done to a depth of 30 cm towards the end of monsoon (October - November). The weeds and vegetative debris are completely turned under and buried in the soil while the stumps are removed. This is known as the cover digging. In slopy areas dig trenches on the contour 45 cm wide and 30 cm deep of any convenient length. Prune water shoots and disease affected shoots.
|
Diseases
Rust
Spray 0.5% Bordeaux mixture in February - March (Pre-bloom) followed by 0.03% Oxycarboxin in May - June (Pre-monsoon). Repeat in July - August (mid-monsoon) September - October (Post-monsoon) with any one of the above fungicides or Spray 0.5 % Bordeaux mixture during the month of June followed by 0.02 % Triadionefon during September and 0.5 % Bordeaux mixture during the month of December.
Rust
Black rot or Koleroga
Centering and handling of the bushes should be done prior to the onset of South-West monsoon. Remove affected twigs. Spray 1% of Bordeaux mixture during break in monsoon.
Collar rot
Treat seeds with Carbendazim 1 g/kg or Carboxin 0.7 g/kg. Maintain filtered shade in nursery. Drench nursery beds with Mancozeb or Captan 0.5 g/lit before sowing.
Brown eye spot
Brown eye spot can be controlled by spraying Captan or Mancozeb or Ferbam 2 g/lit or Carbendazim 0.5 g/lit during September.
Black root rot
Dig out and burn infected bushes. Dig a trench 30 cm deep around affected spot along with a ring of healthy bushes. Prune the healthy bushes within and outside the trench to allow sunlight. Keep the trench free from fallen leaves. Do not replant for 18 months. |
|
Harvest
Harvest starts during November and harvesting extends up to February. Coffee fruits should be harvested as and when they become ripe. Coffee is just ripe when on gently squeezing the fruits the beans inside come out easily. Unripe fruits should be scrupulously sorted out before using the fruits for pulping. They may be dried separately as cherry.
Fly picking: Small scale picking of ripe berries during October to February
Main picking: Well formed and ripened berries are harvested during December. Bulks of the yields are obtained from this picking.
Stripping: Picking of all the berries left irrespective of ripening.
Cleanings: This is collection of fruits that have been dropped during harvesting.
Unripe fruits should be scrupulously sorted out before using the fruits for pulping. They may be dried separately as cherry.
 |
 |
| Immature Berries |
Mature Berries |
Yield
750 - 1000 kg dry parchment /ha
|
|
 |
 |
| Decaffeinated Coffee |
Flavoured Coffee |
|
Market information
|
Growing Districts |
Dindigul, Nilgiris, Salem and Theni |
| Major markets in Tamil Nadu |
Coonoor, Bodinayakanur, Mettupalayam |
| Types |
Arabica, Robusta |
| Grade specification |
Washed, Unwashed, Monsooned, Instant, Ground, Roasted, Speciality |
Source
1. http://lh6.ggpht.com/_KGxfF9paNrY/R8Dnm8KSK4I/AAAAAAAAA-w/Sgae9Iu50w4/IMG_0365.JPG
2. http://www.uga.edu/agsa/Graphics/coffee_nursery.JPG
3. http://www.uga.edu/agsa/Graphics/coffee_nursery.JPG
4. http://www.sgn.cornell.edu/documents/community/feature/200612-2.jpg
5. http://www.apsnet.org/Education/LessonsPlantPath/Coffeerust/Images/fig04.jpg
6. http://www.coffee.uni-bonn.de/images/disease_coffee-rost.gif
|
|

