|
1. THERAPEUTIC DIETS
2. MODIFICATION OF DIETS IN DIFFERENT NUTRIENTS
3. ROUTINE HOSPITAL DIETS
4. SPECIAL FEEDING METHODS
1. THERAPEUTIC DIETS
Top
Therapeutic nutrition is concerned with the nutritional requirements of patients suffering from different diseases and prescribing the right type of diets for them. The objectives of diet therapy are as follows:
i. The correction of the existing dietary deficiencies and to maintain the patient in good nutritional state.
ii. Formulation of the diet to meet the needs of the patient taking into consideration his food habits.
iii. Education of the patient regarding the need for adherence to the prescribed diet.
Diet therapy in most instances is not a remedy in itself but is a measure which supplements or makes the medical or surgical treatment more effective.
FACTORS TO BE CONSIDERED IN PLANNING THERAPEUTIC DIETS
-
The underlying disease conditions which require a change in the diet.
-
The possible duration of the disease.
-
The factors in the diet which must be altered to overcome these conditions.
-
The patient’s tolerance for food by mouth.
-
The normal diet may be modified to
-
Provide change in consistency as in fluid and soft diets.
-
Increase or decrease the energy value.
-
Include greater or lesser amounts of one or more nutrients, for example, high protein, low sodium, etc.
-
Provide foods bland in flavour.
2.MODIFICATION OF DIETS IN DIFFERENT NUTRIENTS
Top
Modifications in diets in diseases may involve changes in different constituents such as
i. Bland diets, omitting spices and condiments.
ii. Low fibre or high fibre diets.
iii. High protein or low protein diets.
iv. High fat or low fat diets.
v. High carbohydrate or low carbohydrate diets.
vi. High calorie or low calorie diets.
vii. Low sodium diets.
The types of changes required in the diets in different diseases are:
MODIFICATION IN CARBOHYDRATE CONTENT
High Carbohydrate diet may be indicated in liver diseases and in pre-operative conditions. Restricted Carbohydrate diet is essential in the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
-
MODIFICATION IN CALORIE CONTENT
Diets with increased calorie content are required in fever, infections and hyperthyroidism. Low calorie diets are used for the treatment of obesity and heart diseases.
-
MODIFICATION IN PROTEIN CONTENT
High protein diets are prescribed in protein – calorie malnutrition, and cirrhosis of the liver. Low protein diet may be necessary in nephritis and hepatic coma.
-
MODIFICATION IN FAT CONTENT
Moderately high fat diet is used in the treatment of severe under-nutrition. Low fat diet is essential in heart diseases, obesity and diseases of the liver.
-
MODIFICATION IN MINERAL CONTENT
High calcium diet is essential in the treatment of rickets and osteomalacia, while a diet restricted in calcium is desirable in kidney stones. Sodium restricted diets are essential in the treatment of hypertension, cardiac failure and kidney diseases.
-
MODIFICATION IN FIBRE CONTENT
Diets rich in fibre are prescribed for the treatment of constipation, while low fibre diets are essential in the treatment of diarrhoea, peptic ulcer and dysentery.
3. ROUTINE HOSPITAL DIETS
Top
1. Clear Fluid Diet
This diet is made up of clear fluids that leave no residue, and it is non gas forming, non irritating and non stimulating to peristaltic action. This diet can meet the requirement of fluids and some minerals and can be given in 1 to 2 hour intervals. The foods which can be included are barley water, dhal water, tea and coffee without milk, etc.
|
|
2. Full Fluid Diet
This diet bridges the gap between the clear fluid and soft diet In this diet, foods which are liquid or which readily become liquid on reaching the stomach are given. It is used following operations, in acute gastritis, acute infections and in diarrhoea. This diet is given at 2 – 4 hours interval. The foods included are kanji, milk shakes, lassi, custards, etc. |
 |
3.Soft Diet
It may be used in acute infections, following surgery, and for patients who are unable to chew. The soft diet is made up of simple, easily digested food and contains no harsh fibre and no rich highly seasoned food. In this diet, three meals with intermediate feedings should be given.
|
 |
4. Regular normal diet
It is most frequently used in all hospitals. it is used for ambulatory and bed patients whose conditions does not necessitate a special diet of one of the routine diets. Many special diets progress ultimately to a regular diet.
|
 |
4.SPECIAL FEEDING METHODS
Top
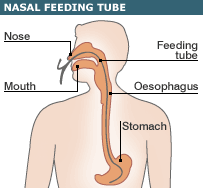
Tube Feeding
This is done by passing a tube into the stomach or duodenum through the nose which is called nasogastric feeding or directly by surgical operation known as gastrostomy and jejunostomy feeding. The type of foods supplied through the tube may be natural liquid foods, solid foods, blenderised to make liquid food commercially supplied polymeric mixtures or elemental diet like Complan, Horlicks, etc., The advantages of tube feeding are Adequate nutrition could easily be given by this method. Foods and drugs which may not be liked by the patients can be administered. |
|
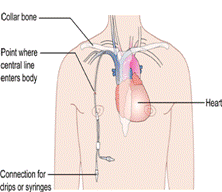
2. Parenteral Feeding
Here the nutrient preparations are given directly into a vein. This method may be used to supplement normal feeding by mouth but can provide all the nutrients necessary to meet a patient’s requirements. Then it is known as total parenteral nutrition or TPN. The nutrients given in TPN are glucose, emulsified fat, crystalline amino acids, Vitamin B12, folic acid and vitamin K, electrolytes like sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium, trace elements like Zinc, Copper, Iodine and Water.
|
|
Source
-
http://www.textbooksonline.tn.nic.in/Books/12/HomeSci-EM/Chapter-3.pdf
-
http://i5.photobucket.com/albums/y152/boo_licious/Porridge.jpg
-
http://www.healthychineserecipes.com/barley_water.jpg
-
http://www.tribuneindia.com/2006/20060430/spectrum/idli.jpg
-
http://www.pseudonews.com/images/tube.gif
-
http://blogs.tastycooks.com/wp-content/uploads/2006/09/img_4280-1.jpg
-
http://www.cancerhelp.org.uk
|
|