Precision Farming
 SOIL
SOIL
 NURSERY
NURSERY
 CROP GEOMETRY
CROP GEOMETRY
 IRRIGATION
IRRIGATION
 FERTIGATION
FERTIGATION
 GROWTH MANAGEMENT
GROWTH MANAGEMENT
 HARVESTING
HARVESTING
 POST HARVEST MANAGEMENT
POST HARVEST MANAGEMENT
 CLUSTER APPROACH
CLUSTER APPROACH
 MARKET LINKAGE
MARKET LINKAGE
 EMPOWERMENT
EMPOWERMENT
Soil
The humus content, microbes, soil aeration and proper drainage must be ensured and fertility status should be restored by the following methods
 |
 |
 |
 |
Green Manure |
Applying Gypsum 2kg per plant |
Neem Cake |
Phosphobacteria |
- Green manure crops viz., Sun hemp must be sown 2 months before planting and during flowering it should be ploughed into soil or
- Green manure crops like, Sesbania or Sun hemp should be sown in alley spaces between the rows of banana plants at the time of planting suckers and incorporate into soil after about 60 days i.e. before seed setting stage.
- Application of Gypsum @ 2 Kg /plant along with 15 Kg of FYM /plant or 45t/ha helps to maintain the soil pH and in turn all major and micro nutrients are available to the plant.
- Application of Potassium Humate @ 25 liters per hectare twice during third and fifth month of planting helps to maintains humus content of the soil.
- Neem cake @ 200 g/ plant + press mud or poultry manure or rice husk ash @ 15 Kg /plant increases not only the humus content of the soil but also controls the nematode population.
- Combination of VAM @ 20 g /plant + Phosphobacteria @ 20 g / plant + Azospirillum @ 50 g / plant + Trichoderma harzianum @ 20 g / plant increases the beneficial microbes in the rhizosphere.
Nursery
Tissue cultured banana seedlings should be selected for planting under precision farming. The tissue culture plants maintains uniformity, fast growing nature and about 20 days earlier in flowering and about 35 days shorter crop cycle with significantly higher yields than suckers. The following points should be considered for the selection of tissue cultured plants.
Selection Criteria
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Proliferation of tissue culture seedlings |
Poly bag filled with soil and potting media |
Seedlings with five leaves |
-
A well hardened plant with minimum of 30 cm in height and should have a pseudo stem circumference of 5.0 – 6.0 cm after 45 – 60 days of hardening should be selected.
-
The plant should have 5 photo synthetically active leaves and inter foliar space must be not less than 5.0 cm.
-
The plant should have approximately 25 – 30 active roots at the end of secondary hardening stage.
-
The length of active roots should be more than 15 cm with a good number of secondary roots.
-
The poly bag should be of size (20 cm in length and 16 cm in diameter) with potting media filled to ¾ full of the bag.
-
The media / potting mixture approximately should weigh about 750 – 800g on dry weight basis.
-
Plant lets should be free from any visual symptoms of leaf spot, pseudo stem rot and physical deformations.
-
Plant lets should be free from the presence of root pathogens like erwinia rot symptoms, nematode lesions and root knots. Random checking of roots is very essential at the time of procurement.
-
Those exhibiting abnormal growth must be discarded.
Crop Geometry
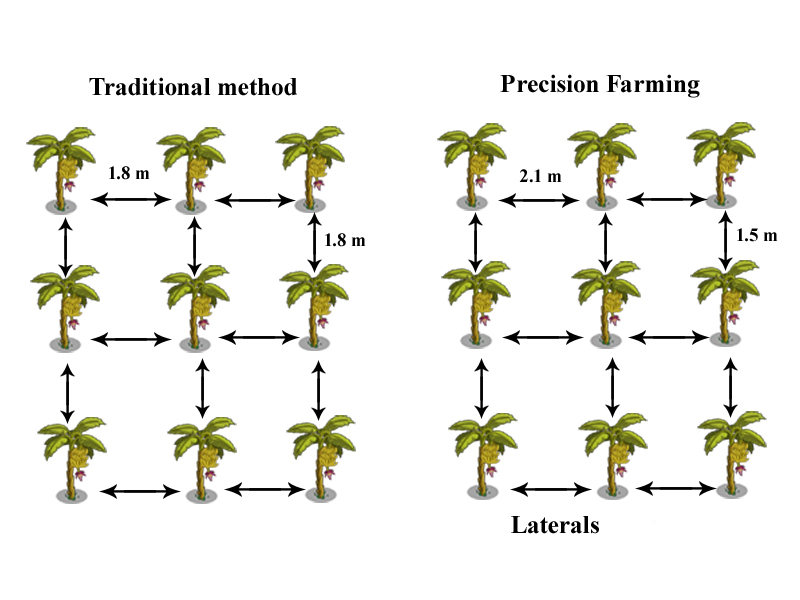
- Crop geometry is highly affected by planting density. The vegetative growth, flowering and fruit growth is not seasonal and are largely influenced by time of planting. Traditionally banana may be planted in 1.8m × 1.8m.
- In Precision farming, laterals placed for banana may be used for vegetables also. Hence, the lateral spacing of 1.5m may be fixed and the banana may be planted in the spacing of 1.5 × 2.1 m and totally around 3175 plants can be planted.
 |
Crop Geometry |
Irrigation
-
In Precision Farming, irrigation is done by drip irrigation system. In sandy loam soil, laterals may be placed @ 6 feet spacing and the drippers of 50 cm or 60 cm may be selected and the water delivery of 3.5 and 4.0 liters per hour respectively. This 6 feet lateral spacing is suitable only for banana.
-
The lateral spacing of 150 cm may be fixed and planting may be done in the spacing of 5 × 7 feet distance.
-
Water requirement for banana plants is about 900 – 1200 for its total duration. For better growth and productivity optimum moisture at all stages of growth and good drainage facility to drain out excess water from the root zone.
-
Under drip irrigation, water is allowed to reach the root zone of the crop in small quantities. Stage wise water requirement of banana is given below
 |
Fertigation
Fertigation is the technique of précised application of dissolved fertilizer to the crops along with irrigation water through appropriate injection device. Through drip irrigation, the water soluble fertilizers and other nutrients can be precisely applied to the soil at appropriate times in desired concentration. These nutrients being placed around the plant roots uniformly and facilitates rapid uptake of nutrients by the plant
Fertigation devices
Water Soluble Fertilizers can be injected into irrigation systems by three principal methods.
- Venturi device.
- Fertigation Tank and
- Displacement pump or Fertigation pump.
Venturi device
Water flowing through the venturi creates a suction that draws the fertilizer solution into the line. This injection method is inaccurate because pressure and flow rates vary in a drip irrigation system.
Fertigation Tank
The fertigation tanks of different sizes viz., 60 l, 90 l, 120 l etc., can be used for fertigation. The pressure difference exists in the input and out put valves sucks the nutrient solution from the tank and pass on to the irrigation pipes.
Fertigation Pump
These inject fertilizer directly into the drip irrigation pipes at a uniform rate. Small electric pumps draw a known volume of solution and force it into the irrigation line.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Fertigation |
Venturi device |
Fertigation tank |
Fertigation pump |
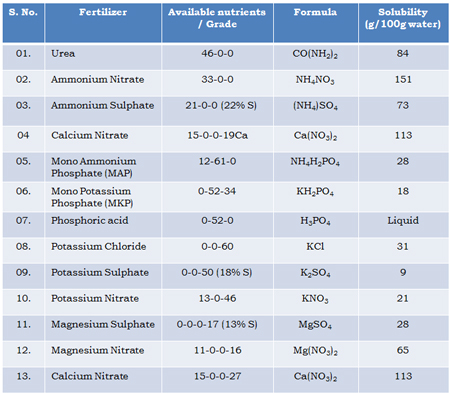
Water Soluble Fertilizers
All the commonly available fertilizers may not be used in fertigation since, they are not 100% soluble. The water soluble solid or liquid fertilizers are highly suitable and the selection of these fertilizers have to meet the following criteria:
- Solubility: The selected fertilizer grade should be 100 per cent soluble and the solubility of fertilizers is reduced when two or three fertilizers are mixed together. When compare the solubility of Nitrogen fertilizers the following should be considered.
- It should avoid corrosion, softening of plastic pipes and clogging of the irrigation system.
- It should not react adversely to salts and other chemicals present in irrigation water.
- It should be completely soluble in water and
- When more than one fertilizer is used, they should not react with each other to form a precipitate.
Commonly available fertilizers used in Fertigation
 |
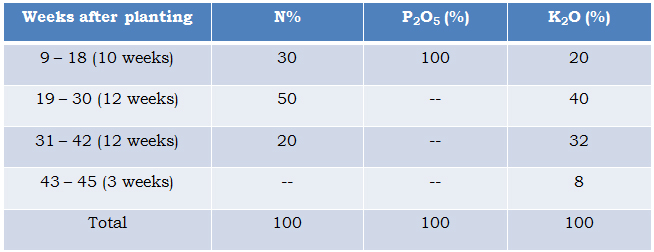
Scheduling of fertigation
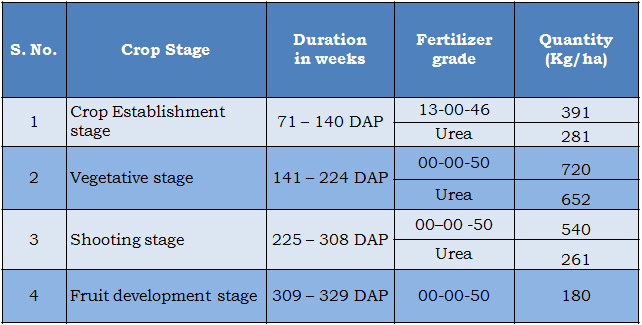
Tissue cultured banana responds well under fertigation and requires 50 per cent extra fertilizers than the suckers planting under conventional system. Application of 200-30-300 g of N: P2O5:K2O /plant using water soluble fertilizers through fertigation is essential. Fertigation should be done at five days interval as per the following schedule
 |
 |
Abstract
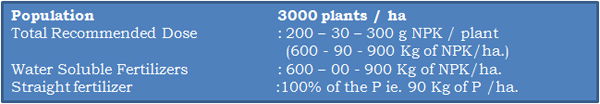
Fertilizer required for one hectare of land
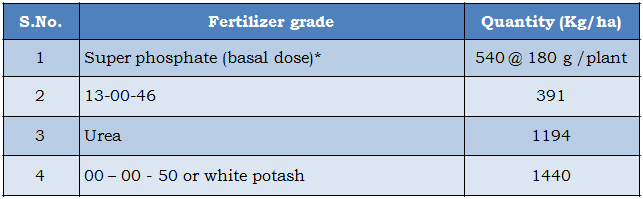 |
Fertigation method:
Three important points should be noticed For effective fertigation scheduling
 |
|
Growth Management
Hi-tech greenhouse:
Optimum growth of plant is governed by the availability and use of natural resources of land, water and sunlight.
In general, greenhouse cultivation could be considered as protected cultivation that enhances the maturity of crop, increases yield, improves the quality of produce and in some instances reduce the use of pesticides. The use of greenhouse technology also reduces the total time for preparation of seedlings and cuttings significantly. Greenhouse is also essential for plant propagation through tissue culture.
 |
 |
 |
Green house |
Tissue culture plant in green house |
Dry leaves mulching |
In-situ moisture conservation:
Mulching is a practice of covering the soil surface around plants to make conditions more conducive for plant growth. Use of dry leaves, straw, hay, stones etc. as mulching material has been prevalent for ages. However, introduction of plastic film as mulch increases the efficiency by improved moisture conservation, increased soil temperature and elimination of weed growth and hence, increase in crop yield. Mulch is also used for soil solarization. It helps to maintain favourable soil temperature during daytime and retains it during night.
Spade digging and earthing up of plants are done after applying 20 g of Furadan + ½ kg Pungam oil cake at 3 MAP.
- Spade digging followed by earthing up is done at 4, 6 and 8 months after planting.
- Desuckering and removal of diseased and dried leaves should be done for 6 times (based on sucker growth).
- Apply 20 g furadon at 4th month after planting.
- Spray zinc sulphate (0.5%), ferrous sulphate (0.2%), copper sulphate (0.2%) and borax (0.1%) at 3, 5 and 7th month after planting.
- Remove male bud - one week after opening of last hand.
- Propping - one month after shoot emergence.
- Intercropping: Inter crops like onion, leafy coriander, beetroot; tomato (variety only) can be grown. Inter cropping should be completed within 90 days of planting of banana. Nematode repelling species like Sun hemp or marigold can be grown and incorporated with soil at maximum vegetative stage.
 |
 |
 |
Plastic film mulching |
Intercropping with Onion |
Propping |
Propping for support :
- Post shooting nutrient spray: Urea 1% and potassium sulphate 1.5% is sprayed after last hand opening and again sprayed at once after a month.
- Bunch cover: The fruit bunches are covered with ventilated (4%) polythene sleeves (200 x 150 cm), ithin 15 days of last hand opening.
 |
 |
Spade digging |
Bunch covering |
HARVESTING
1.Stage of maturity
 |
Bananas are generally mature on 100 to 110 days after shooting of bunches. The fruit bunches are harvested when the angularity of fruits disappears. Mature bananas are not harvested when they are yellow; they are harvested while they are still green, but with a slight yellow tint, which is hardly noticeable. The flower bract is dry and breaks off easily from the fruit tip. When tapped the fruit gives metallic sound. One week before of harvesting, should stop irrigation to the field because it reduces the fruit quality and storage period. Harvesting is to be done based on the selection of market and maturity of banana. Suppose you are going to sell the bunch in local market, harvest at 80-85% maturity and for exporting, harvest at 75% maturity.
2.Harvesting methods
Manual harvesting:
 |
For banana harvesting, one or two workers are needed namely a cutter and a backer. In a large operation, there will be two workers, both the cutter and a backer. In a smaller operation, one person could do the harvesting of banana trees. The cutter is responsible for cutting the banana cluster, cutting down the plant and chopping the stem. After cutting the banana cluster the backer will carry them to the storage shed.
Nylon rope harvesting:
 |
It is one of the advanced technologies in banana harvesting. In this technology, cut the hands separately from the bunch by using thin nylon rope. Put the rope in between the bunch and hands. Then, the hands will be separated easily by pulling the rope. In this method, harvesting is done easily and there is no damage on hands. It is easy to pack and transport to different places.
Post Harvest Management
Bananas can be stored for up to a week in a cool place but unripe bananas should not be stored in the refrigerator, as this may irreversibly interrupt the ripening process. If the banana is no longer green it is ripe and can be stored for a maximum of one week. For storage, banana should be stored at 13° to 14°C
Bunches should be kept out of light after harvest, since this hastens ripening and softening. For export, hands are cut into units of 4 -16 fingers, graded for both length and girths and carefully placed in poly-lined boxes to hold 12 to 18 kg depending on export requirement. Prior to packaging fruits are cleaned in water or dilute sodium hypochlorite solution to remove the latex and treated with thiobendazole.
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Washing |
|
|
Washing:
After separating hands from the bunches, wash the hands in running water to remove the latex. So, the appearance of fruit will be improved. Then, the fruits are dried in open space and taken to cooling chamber.
Grading:
The hands are graded based on the number and size of fingers in each hand. Overripe and injured fruits are discarded at this stage. Banana is sent to the local market as bunches.
Packaging:
- The bunches should then be stacked vertically or horizontally on the ground added with wilted or dry banana leaves in case there is delay in transportation. The bunches are separated by spongy sheet or paper sheets which served as cushion in between the bunches and consequently damage to the fingers during transport is reduced.
- For exports, bananas are removed from the stem and hands and clusters of the bananas are packed in corrugated boxes with perforated polyethylene liners. The curved side of the hands is kept facing upwards making sure that the crown of the upper hands do not damage the banana underneath.
- Keeping quality of banana can be increased when packed in 400 gauge LDPE (low-density polyethylene) bag with or without ventilation either under ambient temperature or in zero energy cool chamber (13.5°C).
Spray growth regulators:
- Spray Gibbrellic acid 150 ppm (150mg in 1 litre of water) + Phenomyl 500 ppm (500 mg in 1 litre of water) + Waxol 6% on banana hands to avoid ripening for 14 days in cooling chamber.
- Dip the banana hands in Gibbrellic acid 500 ppm (500 mg in 1 litre of water) + Chitin (2mg in 1 litre of water) to delay ripening and increase the storage period.
- For fruit ripening, the fruit bunches are sprayed with ethrel 5000 ppm (5ml/lit) with sodium hydroxide pellets.
Storage:
Storing of banana fruits in unvented polybags at low temperature could extend the shelf-life of the fruits. The fruits are stored at 13.5°C in the cooling chamber with 90 to 95% relative humidity. So, the fruits will be kept as unripe and maintain the quality for 20 days. Maintaining ethylene concentration below 1 ppm can extend postharvest life of mature green bananas. Mature-green bananas can be stored for up to 3 weeks in ethylene-free air or up to 6 weeks in a controlled atmosphere at 14°C.
Cluster Approach
The cluster approach is adopted for operational conveniences and to ensure better logistics. This rendered support to collective marketing and mutual consultation and discussions.
 |
 |
|
|
1.How many members are joined to form a cluster?
20 - 25 farmers are joined together to form a cluster. Each farmer possess minimum one hectare of land (2.5 acres) and he is considered as one unit.
2.Is the cluster is scattered or in one place?
The clusters are from one revenue village. If not from two neighbouring villages but not in scattered manner.
3.What is the minimum requirement to join in the cluster?
Each member should have minimum one hectare of land.
4.Is there any possibility to join the farmers having below one hectare of land?
Yes, two or three farmers having less than one hectare can join together and avail one hectare with common water facility.
5. How the clusters are registered as associations?
The group of farmers jointly together as cluster and register as association in registrar of society act.
6. How much subsidy they get from government?
The clusters able to get 65% subsidy from the government. The government gives 40% subsidy as cash and the remaining 25% subsidy as inputs like seeds, fertilizers and pesticides. The clusters approach any company for drip instatallation and submit the quotation to the government. Based on the quotation submitted, the government will give 40% cash subsidy to the clusters.
7. What are the benefits of cluster approach?
- Cluster approach gives social recognition to farmers.
- Helps in obtaining services of both government and private.
- Serves as nodes for exchanging knowledge and information.
- Function as clearing house of information from sources like government, markets, buyers and other associations.
- Clusters serve as demonstration vehicles to disseminate technologies.
- Helps to obtain better value for produce as well as inputs.
- Helps the farmers to buy the inputs directly from the manufacturers cutting the cost down to minimum and strengthened their bargaining power while selling their produce.
- Farmers proficiency in cultivation practices can be achieved.
- Increased the corporate qualities like quantity, quality, uniformity and timely delivery.
- Clusters can play role in monitoring and evaluation and scaling up of effectiveness.
- They can give suggestions in policy making in new developmental activities.
Market Linkage:
- The distribution of banana is effected through growers or producers, preharvest contractors, whole salers, commission agents and retailers.
- The most common market channels seen in banana trade are:
- Producer - wholesaler - retailer - consumer
- Producer - village merchant - wholesaler - retailer - consumer
- Producers - village merchants - retailer - consumer
- Producer - retailer - consumer
- Producer - consumer
Harvesting and assembling the produce for the market is done by
- Growers
- Pre-harvest contractors
- Village merchants.
 |
 |
|
|
i) Growers
- The farmers harvest the crop at periodical intervals and transport to the markets immediately without attaining uniform maturity stage
- The produce is assembled and marketed at the village level itself. Hence, the profit will be reduced due to the intervention of intermediaries.
ii) Pre-harvest contractors
- Pre-harvest contractors are the main assembling agents in the case of bananas. They conduct periodical visits to the banana garden of individual small holdings and enter into contract with these farmers by advancing money to purchase the bunches.
- Hence, the contractor or his subagents assemble them and transport to the main markets.
- Pre harvest contractors operate in and around all the district markets. They are the main financing agents for the farmers.
- Even before all the bunches emerge in the garden, these contractors enter into contract with farmers
- Contract is sometimes fixed on the basis of bunches.
- These merchants advance money to cultivators at the time of entering into contract and go on paying as and when bunches are harvested. Some of the contractors pay only at the end.
- These pre-harvest contractors are the main assembling agency accounting for nearly 80 per cent of the quantity assembled.
iii) Village Merchant
- Village merchant operate in villages near about shandies. These merchants collect the produce and sold at shandies.
These merchants either make outright purchases on cash basis or act as commission agents.
Empowerment
-
The banana farmers need the long term security of fair and stable prices for their fruit in order to continue thefarming sustainably.
-
They also need additional investment income for tackling poverty and improving their communities.
-
For this, the farmers form the clusters and federations at state level. So they will attain social, economical and political empowerment.
Social Empowerment:
-
The precision farmers form federations at state level and registered.
-
From this associations, the farmers strengthen the commodity group based activities, conduct periodical group interactions.
-
Technical knowledge have been equally shared among all the members.
-
By getting high yield, they improve social status in their society.
Economical Empowerment:
- The associations has empowered the farmers to gain better access to the market, collective bargaining has enabled the association to attract the attention of many corporate to come forward to sign trading contracts.
- The input suppliers are made to make presentations on their products and the association is able to procure inputs at distributors rate. They supply inputs in right time and nominal price.
- They develop infrastructures like cold storage, collection centre, procession unit, transport facility etc., through the associations.
- They pool the farmer’s resources to transport the produces to the market, saving time and effort, and guaranteeing delivery.
- The precision farming bananas are rated as super class in all the markets and offered premium prices throughout the year.
- They arrange exposure visits to various post harvest handling units and periodical group interactions have led to more profit realization to the farmers.
- These associations will be helpful to the farmers to improve their economic status.
Political Empowerment::
- The precision farmers associations can able to approach the government for getting subsidies, crop loans, crop insurance schemes etc.,
- Revolving funds also given to associations as same as that of SHGs .
- They can able to participate with central and state government office bearers while preparing new development programmes and give suggestions to change the policies in government.
