|
Bacterial leaf blight
(Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae)
| Symptoms |
|
| |
|
Seedling wilt or kresek
- Observed 1-3 weeks after transplanting
- Green water-soaked layer along the cut portion or leaf tip of leaves as early symptom
- Leaves wilt and roll up and become grayish green to yellow
- Entire plant wilt completely
Leaf blight
- Water-soaked to yellowish stripes on leaf blades or starting at leaf tips with a wavy margin
- Leaves with undulated yellowish white or golden yellow marginal necrosis, drying of leaves back from tip and curling, leaving mid rib intact are the major symptoms.
- Appearance of bacterial ooze that looks like a milky or opaque dewdrop on young lesions early in the morning
- Severely infected leaves tend to dry quickly
- loss in grain yield may be up to 60%.
Confirmation
- To distinguish kresek symptoms from stem borer damage, the lower end of the infected seedling can be squeezed between the fingers.
- Yellowish bacterial ooze may be seen coming out of the cut ends.
- The cut portion can be observed against the light to see the bacterial ooze streaming out from the cut ends into the water.
- After 1-2 hours, the water becomes turbid.
|
|
|
 |
 |
| Seedling wilt-Kresek |
Leaves with wavy yellow
marginal necrosis |
 |
 |
Drying and curling of
leaves leaving midrib
intact |
Affected leaves with wavy
yellow marginal necrosis |
| |
|
|
| Top |
| |
Identification of pathogen |
|
|
 |
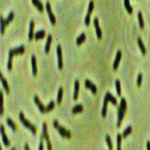 |
- The bacteria causing the disease are rods, 1.2 x 0.3-0.5 µm. They are single, occasionally in pairs but not in chains.
- They are Gram negative, non-spore-forming, and devoid of capsules.
- Their colonies on nutrient agar are pale yellow, circular, and smooth with an entire margin. They are convex and viscid.
Factors favouring disease development
- presence of weeds
- presence of rice stubbles and ratoons of infected plants
- presence of bacteria in the rice paddy and irrigation canals
- warm temperature(25-30° C), , high humidity, rain and deep water.
- Severe winds, which cause wounds, and over fertilization are suitable factors for the development of the disease.
- Irrigation water and splashing or windblown rain can disseminate the bacterium from plant to plant.
- The use of trimming tools for transplanting and by handling during transplanting can also trigger new infection.
|
| Bacterial Ooze |
Microscopic View of
Xanthomonas Oryzae |
 |
| Xanthomonas Oryzae |
|
| Top |
| Management Strategies |
|
|
|
Preventive method
- Seed treatment with bleaching powder (100g/l) and zinc sulfate (2%) reduce bacterial blight.
- Seed treatment - seed soaking for 8 hours in Agrimycin (0.025%) and wettable ceresan (0.05%) followed by hot water treatment for 30 min at 52-54oC;
- seed soaking for 8 hours in ceresan (0.1%) and treat with Streptocyclin (3g in 1 litre);
- Spray neem oil 3% or NSKE 5%
- Spray fresh cowdung extract for the control of bacterial blight. Dissolve 20 g cowdung in one litre of water; allow to settle and sieve. Use supernatant liquid. (starting from initial appearance of the disease and another at fortnightly interval)
|
 |
 |
Soak the Seeds in
Agrimycin for 8 hours |
Spray Fresh Cowdung
Extract |
 |
 |
| |
Spray Neem Oil |
Treat the Seeds with
Bleaching Powder |
|
Cultural methods
- Grow Tolerant varieties (IR 20 IR 72,PONMANI , TKM 6).
- Secure disease free seed
- Grow nurseries preferably in isolated upland conditions
- Avoid clipping of seedlings during transplanting.
- Balanced fertilization, avoid excess N - application
- Skip N - application at booting (if disease is moderate)
- Drain the field (except at flowering stage of the crop)
- Destruction of weeds and collateral hosts
- Avoid flow of water from affected fields
- Maintain proper plant spacing
|
|
|
 |
 |
Avoid Field to Field
Irrigation |
Maintain Proper Spacing |
|
Chemical methods
- Seed treatment with bleaching powder (100g/l) and zinc sulfate (2%) reduce bacterial blight.
- Seed treatment - seed soaking for 8 hours in Agrimycin (0.025%) and wettable ceresan (0.05%) followed by hot water treatment for 30 min at 52-54oC;
- seed soaking for 8 hours in ceresan (0.1%) and treat with Streptocyclin (3g in 1 litre);
- Spray Streptomycin sulphate + Tetracycline combination 300 g + Copper oxychloride 1.25kg/ha. If necessary repeat 15 days later.
- Application of bleaching powder @ 5 kg/ha in the irrigation water is recommended in the kresek stage.
- Foliar spray with copper fungicides alternatively with Strepto-cyclin (250 ppm) to check secondary spread.
|
|
|
 |
 |
| Foliar Spraying of Copper Fungicides |
Seed Treatment with Zinc Sulphate |
| |
| Top |
|















