|
 |
| Germination stage |
| Name of the disease | Symptoms |
Management |
Image |
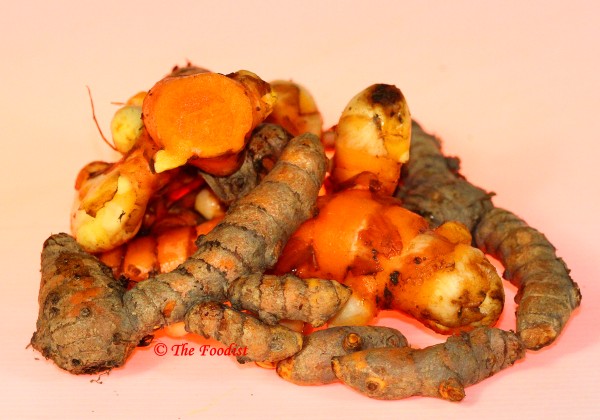
Rhizome rot – Pythium aphanidermatum, P. graminicolum The disease is common in Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu. Disease cycle • Priamary Infectiion(P.I): The fungi survive in soil and infected rhizomes as oospores • Secondary Infection (S.I): Spreads through irrigation water as zoospores |
• The disease occurs in patches. Infected plants show progressive drying up of the leave, which first proceeds along the margins and later the entire leaf dries up
• Infection gradually spreads to rhizomes which begin to rot and become soft.
|
• Crop rotation with non-hosts
• Grow turmeric in light soils with good drainage
• Use disease free rhizomes for planting
• Rhizomes should be dipped in Metalaxyl@2.5g/l or Bordeaux mixture@1% solution for 40 minutes
• Drench the soil at root region with captan@2 g or COC@2.5 g or metalaxyl@1 g per liter in the initial stages of the disease
• Grow resistant varieties to this disease. |
|
| Vegetative growth stage |
| Parts affected | Symptoms |
Management |
Image |
| Panicles, leaves and stem | • The adult and nymphs of ho Nymphs and adults suck sap from leaf surface causing yellowing of leaves in patches which dry and drop off. • Black resinous excretion in tiny spots are seen between the damaged areas. |
• Foliar spray with malathion 2ml/l or methyl demeton 2ml/l, or dimethoate 2 ml/l is effective. |  |
| Parts affected | Symptoms |
Management |
Image |
| Panicles, leaves and stem | • Nymphs and adults suck the sap from leaves. • The affected leaves roll up, turn pale and gradually dry up. • The pest infestation is more common during the post monsoon period especially in the drier parts of the country. |
• Spraying of dimethoate 0.05%, is effective for the management of the pest. • Spray insecticides like quinalphos 0.025% or fenthion or phosalone 0.07% |
 |
| Parts affected | Symptoms |
Management |
Image |
| Panicles, leaves and stem | • • The larvae bore into pseudostems and feed on internal tissues resulting in yellowing and drying of leaves of infested pseudostems. • The presence of a bore-hole on the pseudostem through which frass is extruded • Withered and yellow central shoot is a characteristic symptom of pest infestation. |
• Spraying malathion 0.1% at 30 day intervals during July to October is effective in controlling the pest infestation. • The spraying has to be initiated when the first symptom of pest attack is seen on the inner most leaves on the pseudostem. |
 |
| Parts affected | Symptoms |
Management |
Image |
Leaves |
• Larvae Feeds from inside the leaf, folds and pupates inside the leaf |
• Hand pick the larvae and pupae • Spray 0.5% of Dimethoate or Phosphomidan |
|
| Parts affected | Symptoms |
Management |
Image |
Rhizome |
• It infests rhizomes in the field (at later stages of the crop) and in storage. • Rhizomes become shriveled and desiccated affecting its germination at severe attack. • Adult (female) scales are circular (about 1mm diameter) and light brown to gray and appear as encrustations on the rhizomes. |
• Rhizomes become shriveled and desiccated affecting its germination at severe attack. • Treat seed material with quinalphos 0.075% (for 20-30 minutes) before storage and also before sowing in case the infestation persists. • Discard and do not store severely infested rhizomes. |
|
| Name of the disease | Symptoms |
Management |
Image |
Leaf spot – Colletotrichum capsici Disease cycle • P.I: Infected plant debris • S.I: Air borne conidia | • Fungus attacks only leaves and usually infection is confined to leaf blades and occasionally extend to leaf sheaths
• On leaves, elliptic to oblong spots of different sizes appear on both the surfaces, but more on upper surface
• Spots gradually increase in size and attain a length of 4-5cm and breadth of 2-3cm
• Mature spots have grayish center with dark brown margins surrounded by a yellow halo.
• Central portion of the spot becomes thin and papery
• Several spots coalesce to form irregular necrotic patches
|
• Remove and destroy infected plant debris
• Treat rhizomes with COC@0.25% solution
• Spray Carbendazim@0.1% or Mancozeb@0.25%. during Aug-Dec along with sandovit@0.5 ml/lt
• Avoid excess shading
• Grow tolerant varieties to this disease |
|
| Name of the disease | Symptoms |
Management |
Image |
Leaf blotch – Taphrina maculans • Survival and spread: Infected plant debris |
• Appearance of large number of spots on both surfaces of leaf • Spots first appear as pale yellow discolouration which gradually turn to reddish brown • Spots lie between leaf veins and are rectangular, coalesce to form big irregular patches |
• Grow resistant varieties |
|
![]()
Focus Districts
Gallery