|
False Smut
(Ustilaginoidea virens)
| Symptoms |
|
| |
|
- Individual rice grain transformed into a mass of yellow fruiting bodies
- Growth of velvetty spores that enclose floral parts
- Infected grain has greenish smut balls with a velvetty appearance.
- The smut ball appears small at first and grows gradually up to the size of 1 cm.
- It is seen in between the hulls and encloses the floral parts.
- Only few grains in a panicle are usually infected and the rest are normal.
- As the fungi growth intensifies, the smut ball bursts and becomes orange then later yellowish-green or greenish-black in color.
- Infection usually occurs during the reproductive and ripening stages, infecting a few grains in the panicle and leaving the rest healthy.
|
 |
 |
| Discolouration of Grains |
Grains Transformed into a
Mass of Yellow Fruiting
Bodies |
 |
 |
Greenish Black Smut Balls
with a Velvetty Appearance |
Smut Balls Bursts and
becomes Black in Color |
|
| Top |
| |
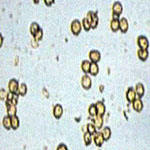
Identification of pathogen |
|
|
 |
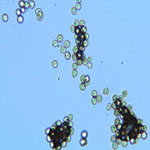 |
- Chlamydospore formed on the spore balls are born laterally on minute sterigmata on radial hyphae, and are spherical to elliptical, warty, olivaceous, 3-5 x 4-6 µm. Younger spores are smaller, paler, and almost smooth.
- Some of the green spore balls develop one to four sclerotia in the center. These sclerotia overwinter in the field and produce stalked stromata the following summer or autumn.
- In temperate regions, the fungus survives the winter by means of sclerotia as well as chlamydospores.
- It is believed that the primary infections are initiated mainly by the ascospores produced from the sclerotia.
- Chlamydospores play an important role in secondary infection, which is a major part of the disease cycle.
Conditions that favour disease development
- presence of rain and high humidity
- presence of soils with high nitrogen content
- presence of wind for dissemination of the spores from plant to plant
- presence of overwintering fungus as sclerotia and chlamydospores
- flowering stage of the rice crop
|
| False Smut Spores |
Microscopic View of
Spores |
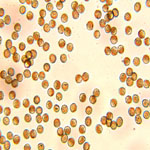 |
| Ustilaginoidea Virens Spores from Infected Rice Grain |
|
| Top |
| Management Strategies |
|
|
|
Preventive methods
- Use of disease-free seeds that are selected from healthy crop.
- Seed treatment with carbendazim 2.0g/kg of seeds.
- Control insect pests.
- Split application of nitrogen is recommended.
- Removal and proper disposal of infected plant debris.
|
 |
 |
| Use Dieases Free Seeds |
Seed Treatment with
Carbendazim |
|
Cultural methods
- Among the cultural control, destruction of straw and stubble from infected plants is recommended to reduce the disease.
- Use varieties that are found to be resistant or tolerant against the disease in India.
- Avoid field activities when the plants are wet.
- Early planted crop has less smut balls than the late planted crop.
- At the time of harvesting, diseased plants should be removed and destroyed so that sclerotia do not fall in the field. This will reduce primary inoculum for the next crop.
- Field bunds and irrigation channels should be kept clean to eliminate alternate hosts.
- Excess application of nitrogenous fertilizer should be avoided.
- Regular monitoring of disease incidence during rabi season is very essential.
- Proper Destruction of straw and stubble.
|
 |
 |
Destruction of Straw and
Stubbles |
Keep Irrigation Channel
Clean |
| |
|
 |
 |
| Keep the Bunds Clean |
Use LCC to Avoid Excess
Application of Nitrogen |
|
Chemical methods
- Spraying of copper oxychloride at 2.5 g/litre or Propiconazole at 1.0 ml/litre at boot leaf and milky stages will be more useful to prevent the fungal infection.
- Seed treatment with carbendazim 2.0g/kg of seeds.
- At tillering and preflowering stages, spray Hexaconazole @ 1ml/lit or Chlorothalonil 2g/lit.
- In areas where the disease may cause yield loss, applying captan, captafol, fentin hydroxide, and mancozeb can be inhibited conidial germination.
- At tillering and preflowering stages, spraying of carbendazim fungicide and copper base fungicide can effectively control the disease.
|
|
|
 |
 |
| Spray Copper Oxychloride |
Spray Hexaconazole |
| |
Top |
|















