|
Grain Discoloration
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | ||
|
 |
 |
| Discolouration of grains | Bblack Spots Appear on Grains with Prominent Fungal Discolouration |
|
 |
 |
|
| Black Spots Appear on Grains |
Fungal Growth on Grains | |
| Top | ||
| Identification of pathogen | ||
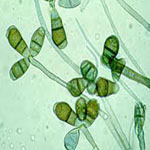 |
.jpg) |
Group of fungus
Favourable Conditions:
|
| Curvularia Lunata Spores | Filamentous Fungus (Fusarium Monoliforme) |
|
| Top | ||
| Management Strategies | ||
Preventive methods
|
 |
 |
| Use Dieases Free Seeds | Seed Treatment with Carbendazim |
|
Chemical methods
|
 |
 |
| Captan | Spray Mancozeb at Boot Leaf Stage | |
| Top | ||
