|
Ragged stunt virus
| Symptoms |
|
|
|
- Infected plants severely stunted during early growth stages of the crop
- Leaves short and dark green with serrated edges
- Leaf blades twisted at the apex or base, which result in the spiral shape of the leaves
- Leaf edges uneven and the twisting give the leaves a ragged appearance
- Ragged portions of the leaves are yellow to yellow-brown
- Vein swellings develop on the leaf blades and sheaths
- Swellings pale yellow or white to dark brown
- Flag leaves twisted, malformed, and shortened at booting stage
- Flowering is delayed
- Incomplete panicle emergence
- Nodal branches produced at upper nodes
- Partially exserted panicles and unfilled grains
|
 |
 |
| Ragged Stunt Virus |
Rice Ragged Stunt Disease |
| |
|
|
| Top |
| |
Identification of pathogen |
|
|
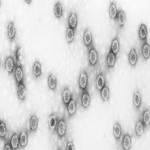 |
The brown planthopper transmits the disease. The early instar nymphs of the insect are more efficient in transmitting the disease than older ones. Five-day-old nymphs are the most efficient transmitters. The virus is acquired within a feeding period of 24 hours.
Viral particles are 63-65 nm in diameter and consist of five proteins. They are mostly found in phloem and gall cells. The genome consists of ten double-stranded RNA segments.
The virus is circulative and propagative in the insect vectors. |
| Ragged Stunt Causal Virus |
|
| Top |
| Management Strategies |
|
|
|
- Avoid close planting and provide 30 cm rogue spacing at every 2.5 to 3.0 m to reduce the pest incidence.
- There are varieties released by IRRI, which contain genes for BPH resistance, like IR26, IR64, IR36, IR56, and IR72.
- plouging and harrowing the field to destroy stubbles right after harvest in order to eradicate other hosts.
- Apply any one of the following to control vector BPH:
Phosphamidon 40 SL 1000 ml/ha (or) Phosalone 35 EC 1500 ml/ha (or) Carbaryl 10 D 25 kg/ha (or) (or) Acephate 75 SP 625 gm/ha (or) Chlorpyriphos 20 EC 1250 ml/ha. |
 |
| Ploughing to Incorporate Stubbles |
| |
Top |
|