|
Udbatta Disease
| Symptoms |
|
| |
|
- A white mycelial mat ties panicle branches together so that panicle emerge as single, straight, dirty coloured, cylindrical rods much resembling an agarbatti or udbattta, hence the name.
- White mycelium and conidia form narrow stripes on the flag leaves along the veins before the panicles emerge. No grains are formed on the affected ear.
- The diseased plants produce distorted earheads later. Infection of the seeds is initiated at the time of emergence of the panicle
- It is reported to occur in severe forms in many parts of South India, including Madurai district in Tamil Nadu, Wynaad in Kerala and Kollegal and South Kanara districts in Karnataka.
|
 |
 |
Distorted Panicle with
White Mycelium and
Conidia |
Panicle Emerge as Straight
Dirty Coloured Cylindrical
Rods as Udbathi |
|
| Top |
| |
Identification of pathogen |
|
|
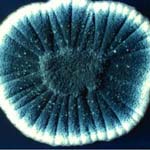 |
Perfect Stage: Balansia oryzae – sativae. Hashioka. (Subdivision: Ascomycotina; Order: Sphaeriales; Family: Hypocreaceae). The perfect stage of the fungus is an Ascoycete, Balansia oryzae-sativa.
Disease Cycle:
- The fungus is seed-borne externally and systemic.
- The presence of lustrous grayish white films of fungal growth in young leaves of the infected seedlings suggest the entry of the pathogen during germination of the seeds.
- As no grains are obtained from aggected heads, diseased seeds are not important in perpetuation of the disease.
- The fungus has been recorded on the grasses Isachne elegans, Cynadon dactylon, Pennisetum sp., and Eragrostis tenuifolia and they serve as collateral hosts.
- The disease incidence is less severe on very early and late sown crops.
Factors favoring disease development
- Presence of the bacteria on leaves and in the water or those surviving in the debris left after harvest
- Warm temperature and high humidity
- Early stage of planting from maximum tillering to panicle initiation
|
Ascomycete of Euphelis
Oryzae |
|
|
 |
Microscopic View of
Fungus Ephelis Oryzae |
|
| Top |
| Management Strategies |
|
|
|
- Use disease free seeds for sowing.
- Seed treatment with Captan or Thiram.
- Hot water treatment of the seeds at 50-540 C for 10 minutes before sowing gives effective control of the disease.
- Solar treatment of seeds is effective in killing the pathogen carried in the seeds, if any.
- It is also advisable to avoid using seeds from fields where the disease is noted.
- Removal and destruction of diseased panicles in field.
|
 |
 |
Seed Treatment with
Captan |
Solar Treatment of Seeds |
| Top |
|